CBI has designed and launched a new Data Basin Gateway (Atlas) for the Wildlife Conservation Society Canada focusing on the Yukon Territory to assist WCS Canada researchers and their conservation partners in the region to develop effective protection of wildlife and plants being impacted by a host of environmental stressors, with special emphasis on climate change. In addition to the branded and curated gateway with relevant datasets, we have co-produced a customized application for stakeholders to view and download species distribution models (SDM) for 66 endemic plants designed to predict future changes in their distribution due to climate change. The Atlas houses relevant datasets for conservation planning in the climate-sensitive Yukon region and the tool houses the SDMs, which in combination provide powerful resources for WCS Canada and its partners to effectively plan for resilience.
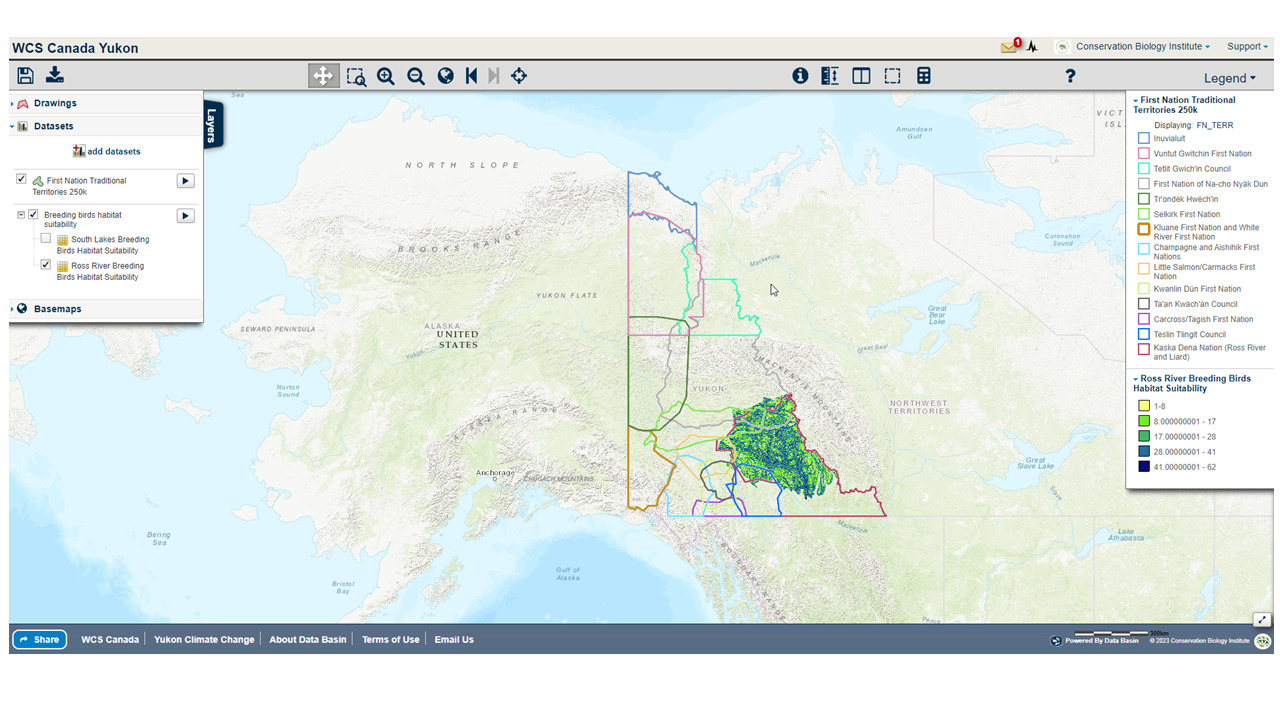
An example of a map created in the WCS Yukon Data Basin Atlas showing First Nation Territories overlaid on Ross river breeding bird habitat suitability layer
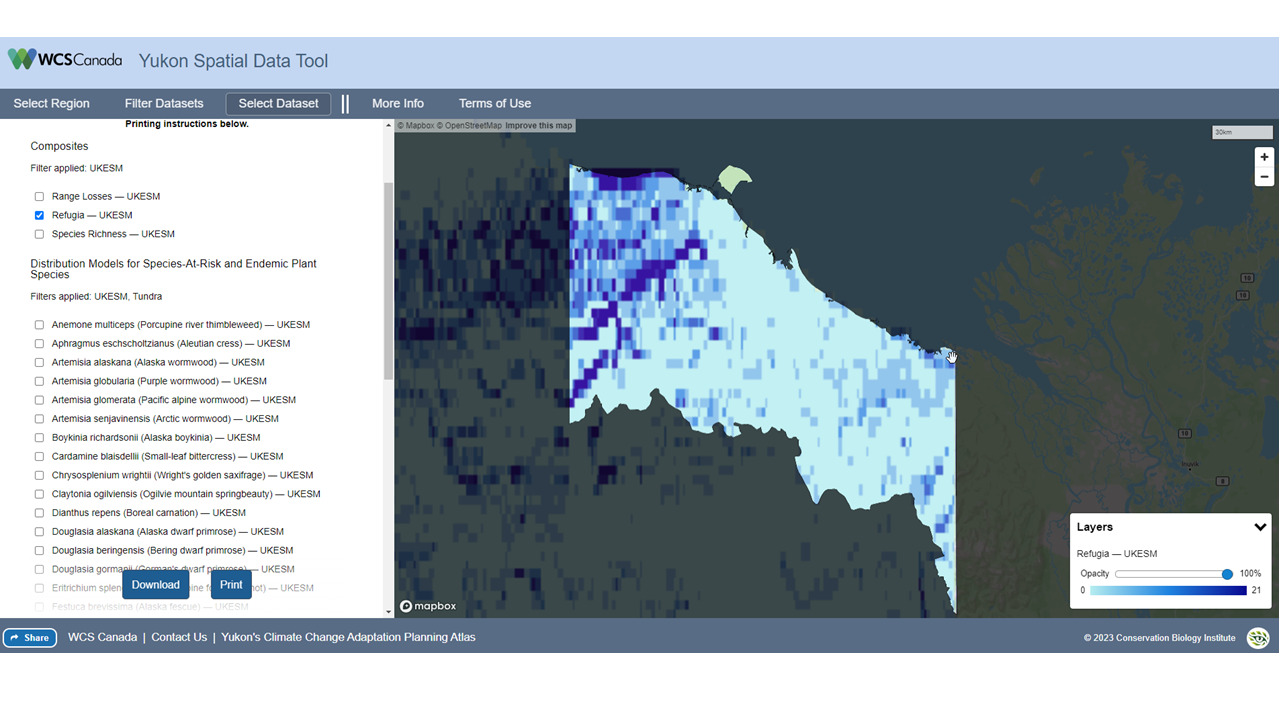
The Yukon Spatial data tool showing projected climate refugia for a Inuvialuit Planning region in the Yukon
As the Sierra Nevada town of Paradise rebuilds after the devastating Camp Fire of 2018, the community has an opportunity to incorporate strategies to increase its resilience to fire and climate change, enhance the safety and well-being of its residents, and at the same time care for the surrounding natural areas that make it a beautiful place to live.
CBI and the The Nature Conservancy helped Paradise seize this opportunity when the Paradise Recreation and Park District asked us to help them explore community design principles that could provide all of these benefits. The CBI team created geographic models of “Wildfire Risk Reduction Buffers” between the structures and the surrounding wildlands to reduce exposure of homes to wildfire risks. These buffers, which can be made up of parklands, orchards, and other low fire-risk land uses, can be managed to provide many benefits, including buffering homes from ignition, providing safe-haven refuges for residents to escape from fire, strategically-placed staging areas for fire-fighters, recreational access to open space, and protecting natural habitat from the effects of an encroaching urban landscape.
The team combined spatial data about the landscape with local knowledge to prioritize locations for fire risk-reduction and analyzed ignition risks and co-benefits with and without the buffers. The resulting maps illustrate the potential for local partnerships to make a real difference in the town’s future. Through innovative thinking about the role of land use planning, the community of Paradise is changing its approach to living with fire and providing a model for fire-prone communities everywhere.
CBI is supporting the U.S. Forest Service (Region 8) in its efforts toward shared forest stewardship activities. Region 8 contains approximately 244 million acres of forestland, most of which (87%) is privately owned. The Forest Service manages around 5% of the southern forests within 14 National Forests and two Special Units with other public forests make up the remaining 8%. Because of the mixed ownership, close collaboration and shared stewardship is of paramount importance.
CBI has created a customized and curated Data Basin Gateway for the U.S. Forest Service (usfssouth.databasin.org) that supports forest stewardship organizations to access data and information to advance collaborative forest management planning. To demonstrate how to use this framework, a pilot state (North Carolina) was chosen (nc.usfssouth.databasin.org). This gateway uses the “All Lands Strategy” concept to showcase example workflows to facilitate more effective forest management and monitoring across North Carolina. CBI and the North Carolina Shared Stewardship team created supporting training materials is the form of video tutorials and how to materials.
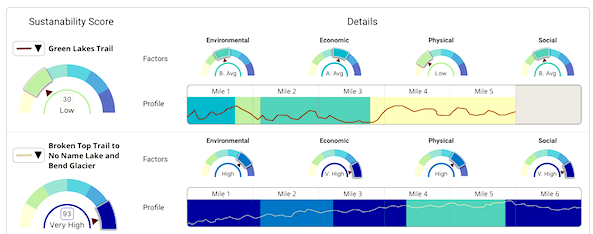
The Conservation Biology Institute’s recent work with the Deschutes Trails Coalition (DTC) and the Deschutes National Forest focuses on designing a Trails Assessment and Planning Tool for Deschutes County. We have developed a blueprint for the design, in collaboration with the U.S. Forest Service and the DTC. In this new phase of the project, funded by the U.S. Forest Service, CBI will partner with the DTC to build a prototype of the trails decision-support tool and sustainability model for Deschutes County. Then we will scale up and customize this prototype to meet the requirements of the U.S. Forest Service and its partners in the states of Oregon and Washington. The Trail Assessment and Planning Tool design includes creating a preliminary version of a sustainability framework that incorporates an interactive spatially-explicit model, addressing the physical, environmental, social, and economic aspects of sustainability. The model is powered by CBI’s Environmental Evaluation Modelling System (EEMS), allowing for its collaborative development with a diverse group of stakeholders, to create a transparent framework for local, regional, and national organizations to answer important questions relevant to trails planning and management.


Proxy Falls, Oregon
Michael Riffle / Flickr
In 2006, the Micronesia Challenge began as a commitment by the Republic of Palau, Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Federated State of Micronesia, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands to preserve the marine and terrestrial resources crucial to the survival of the Pacific traditions, cultures, and livelihoods. The overall goal of the initial Micronesia Challenge was to effectively conserve at least 30% of the near-shore marine resources and 20% of the terrestrial resources across Micronesia by 2020.
During the 24th Micronesia Island Forum in 2019, the regional leadership recognized the success of the first 15 years of the Micronesia Challenge and endorsed the new Micronesia Challenge 2030 goals to effectively manage 50% of the marine resources and 30% of terrestrial resources by 2030.
In 2016, the USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) team, regional partners and CBI developed the Micronesia Challenge Regional Terrestrial Monitoring Initiative tool (mcterrestrialmeasures.org) to allow users to visualize the spatial data from the Micronesia Challenge monitoring effort by regional framework indicator(s) that measure the status of managed conservation areas set aside under the program. The first version of the tool included forest data collected between 2003 and 2018 and determined the status and trends in forest area, forest health, understory vegetation, biomass, and carbon storage.
In this new phase of work, the Terrestrial Measure Initiative tool will be updated with the most recent data and information. The team also plans to develop a webinar presentation to communicate with local stakeholders and others about the tool and the ongoing success of the Micronesia Challenge.
The USDA Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) works with farmers and landowners to implement conservation management practices on enrolled lands, with paid contracts ranging from 10 to 15 years in length. The CRP Grasslands practices target restoration of agricultural grassland systems by augmenting native vegetation for pollinators, providing habitat for grassland plants and animals, increasing biodiversity, reducing soil erosion, and improving water quality. The USDA’s CRP has been successful in improving the conservation value of millions of acres of farmlands; however, the program currently lacks spatially explicit information on land cover and vegetation within CRP-enrolled tracts.
In partnership with the USDA FSA program, the Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) used a combination of remote sensing and machine learning algorithms deployed on the innovative cloud-computing platform, Google Earth Engine, to map grassland characteristics. We used a rich suite of enviro-climatic data, multiple sources of satellite imagery, and Random Forest modeling techniques to predict land cover for study areas in Washington, Colorado, and Kansas, where CRP Grasslands holdings are most prevalent. We used machine learning to create predictive maps of vegetation type by leveraging an extensive set of satellite-derived variables, environmental layers, and federal survey data (from BLM’s AIM and USDA NRCS’s NRI programs). Our initial investigation utilized Landsat 8 satellite data to model vegetation cover across the Washington study area and then scaled up to the Colorado-Kansas study area. The Washington study site was selected for further model enhancements and an in-depth comparison of Landsat 8, Sentinel-2, and MODIS satellite imagery, to evaluate differences in model development and performance among sensor types. We generated vegetation cover predictions for the year 2019 using Random Forest classification models. Classified outputs for the five vegetation cover models – annual grass, perennial grass, annual forb, perennial forb, and bare soil – were post-processed to exclude water and urban land cover and areas that were not relevant for mapping grasslands.
Mapped outputs showing vegetation percent cover predictions from our pilot project have been integrated into CBI’s CRP online decision support tool. This online tool offers functionality for managers and landowners to view, filter, compare and summarize geospatial information relevant for assessing CRP tracts in the study areas. You will need permission from USDA to use the tool, but it is available at https://crptool.org/. Anyone can view the design of the tool at USDA CRPtool.
You can read more details in the following publication.
Degagne, Rebecca; Pizzino, Declan; Friedrich, Hannah; Gough, Mike; Joseph, Gladwin; Strittholt, James; et al. (2022): Mapping Conservation Reserve Program Grasslands in Washington, Colorado, and Kansas with Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. figshare. Journal contribution. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.19141853.v1

The Conservation Biology Institute and the Deschutes Trails Coalition (DTC) are in the process of developing a web-based system to assist the DTC in sustainably managing multi-use trails in Deschutes County. The collaborative process of creating a framework to support DTC’s decision making relies on modeling Environmental, Economic, Physical, and Social Sustainability of recreation activities and trails.
*Images provided by Danielle MacBain at the Deschutes Trails Coalition.
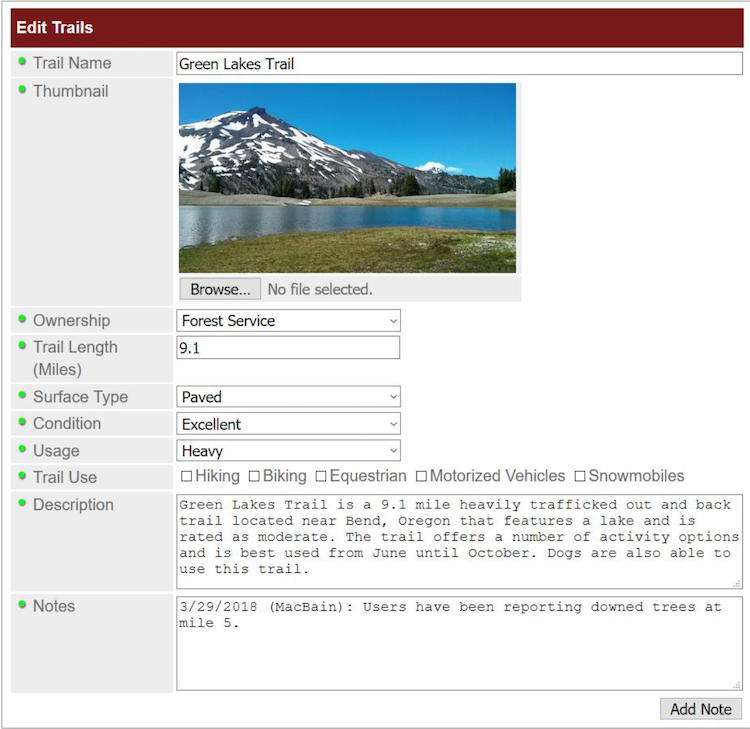
*The DTC Dashboard will include a form-based system to give users the ability to enter or modify information in the trails database.
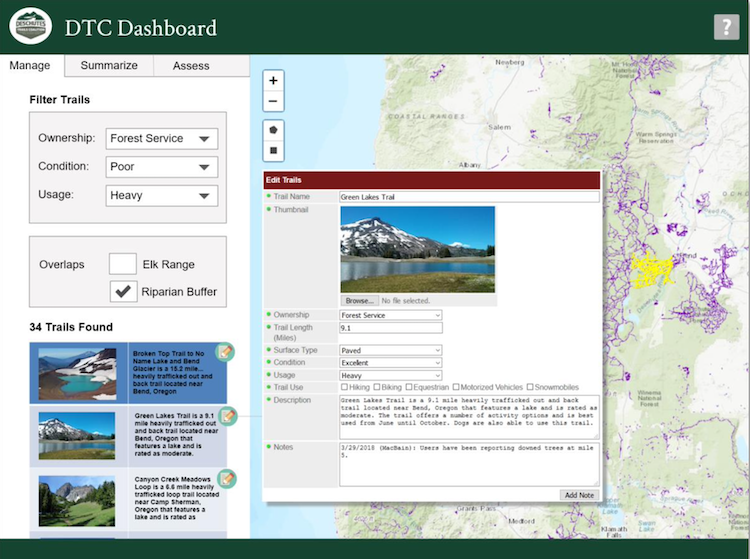
*Mockup of the DTC Dashboard (Query Tools on the Manage Tab)


Wind energy developed in federal ocean waters off California’s coastline is poised to play an important role in diversifying the portfolio of resources that will help California achieve its 100% renewable and zero-carbon energy goals. Since 2016, the state has coordinated with other governmental partners, including the BOEM-California Renewable Energy Intergovernmental Task Force, to identify areas in federal waters off the state’s coast suitable for potential offshore wind energy development. To support this effort, the Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) is using data from the California Offshore Wind Energy Gateway to produce a robust set of spatial models, designed to synthesize information to help stakeholders and decision-makers assess the suitability of offshore wind energy development in federal waters off the coast of California. These models, created using the Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (EEMS), provide a transparent and data-driven means for assessing a range of considerations at a given location, such as existing energy potential, deployment feasibility, ocean uses, fisheries, and marine life occurrence. Together, these models can be used to inform planning processes for offshore wind energy development to maximize renewable power generation and to avoid or minimize impacts to existing ocean uses and the environment.
The California Offshore Wind Energy Modeling Platform, powered by EEMS Online technology, provides an interface where stakeholders and decision-makers can interact with and explore the models and their data sources to help support decision-making processes.
The project’s technical report, executive summary, and presentation slides are available under “Project Files”, on the right side of this page. A California Energy Commission webinar recording with a project overview can be found here.
Conservation Biology Institute specializes in harnessing the power of spatial data for conservation planning and decision-making. We create tools in close collaboration with state agencies that help them achieve their missions. Recently we’ve had the opportunity to work with the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA).
The CDFA Healthy Soils Program promotes the development of healthy soils on California’s farmlands and ranch lands by providing financial incentives to California growers and ranchers to implement agricultural management practices that sequester carbon, reduce atmospheric GHGs and improve soil health.
Conservation Biology Institute created the CDFA Healthy Soils Program tool, an online tool to streamline the submission process for proposals to the Healthy Soils Program. This tool, a custom module of RePlan, allows a grant recipient to locate and map proposed conservation practices, view and select from recommended species for planting, and conform with multiple project eligibility requirements. All project components are then summarized in a proposal report for upload to the CDFA Healthy Soils Program project submission website.
*Find the tool here: https://sitecheck.opr.ca.gov/
CBI developed the tool for the Governor’s Office of Planning and Research (OPR) in coordination with the Department of Housing and Community Development. The tool was developed in partnership with OPR and is based on public input from partners through interviews, presentations, and workshops. Site Check is an innovative mapping tool that allows users to see if selected parcels may qualify for an existing streamlining option for housing development. The free tool allows users to map various CEQA definitions and filter parcels based on planning, transportation, and environmental criteria. Site Check is a good first step for developers and public agencies considering how California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA) may apply to a housing project. Check out the free tool here Site Check.
This tool is focused on the CEQA provisions that cover a variety of housing types. The Legislature has also created specialized provisions for specific types of projects, including affordable housing, agricultural employee housing, and motel-to-supportive housing conversions.
CBI updated the UI for the tool in 2023 and updated data, including the regional below-average Vehicle Miles Traveled (VMT), 15% below regional average VMT, parcel data, Specific Plans. Check these layers out in the tool or download them from Data Basin.
If you have any questions about Site Check, please feel free to contact Brianne Masukawa, brianne.masukawa@opr.ca.gov.
