Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) and American Farmland Trust (AFT), the organization behind the national movement No Farms No Food®, continue to build off their previous work on the San Joaquin Land and Water Strategy. With the support from a Conservation Innovation Grant by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, this phase of work focused on identifying priority areas for groundwater recharge in Madera and Stanislaus counties as well as the greater San Joaquin Valley.
CBI and AFT have compiled informative datasets related to soils, crop types, water infrastructure, and conservation areas in the San Joaquin Valley. These will be located in a San Joaquin Valley Gateway Gallery and mapping tool (with an associated manual) to aid in identifying optimal projects with the greatest potential to increase infiltration and conserve water. These datasets will provide a broad context that will allow for multiple benefits where possible such as locating conservation easements near currently protected areas in the productive farmland regions of Madera and Stanislaus counties, California.
The Project Prioritization Tool (PPT) is a conservation decision-making tool to increase the adoption of water infiltration practices, improve groundwater recharge, and protect agricultural land in the San Joaquin Valley (SJV). This PPT manual was developed by AFT and the Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) based on the data analysis of the San Joaquin Land and Water Strategy report.
In this project, CBI is a member of and also providing support to the Fort Bragg Headlands Consortium, with a mission to to help achieve environmentally sound restoration and development solutions that will improve the quality of life and economy for current and future residents of our Coast.
CBI’s major contribution to the Consortium is to develop and maintain the Fort Bragg Headlands web-mapping Gallery. Powered by Data Basin, this web-mapping Gallery is a feature-rich platform for local citizens, stakeholders and decision-makers to access publicly available spatial data (e.g. maps of streams, wetlands, hazards, soils, geology, etc.). This is timely, as Fort Bragg is currently making a significant Local Coastal Program (LCP) Amendment. Currently zoned Forest Light Industrial, these zoning changes will make the third of the city that was once a lumber mill into prime real estate zoned for profitable development. Fort Bragg is also figuring out how to deal with the remaining wetlands out there that still contain hazardous materials despite a first round of clean-up by the landowner. Providing easy access to data and maps will facilitate decisions that conserve the landscapes and biodiversity of the Fort Bragg region while bringing much needed development and jobs to sustain current and future generations. You can donate directly to this cause here.
Wildfires are a natural part of California ecosystems and play an important role in maintaining ecological structure and function. However, different fire regimes in the state have been altered due to past management practices, climate change, invasive species, and population growth and urban expansion. Given the potential for conflicts between fire management and conserving biodiversity and ecological functioning, solutions are needed to balance ecosystem health with human welfare and community safety.
CBI is partnering with Dr. Jon Keeley (USGS) and an international team of landscape ecologists, biologists, geographers and economists to study the factors that control wildfire activity in southern California, which experiences the largest number of housing losses to wildfire in the U.S. This work focuses on the role of different ignition sources, climate patterns, vegetation change, and housing location and arrangement in altering fire patterns and contributing to housing loss at the wildland-urban interface. Other topics of research include the effectiveness and effects of fuel treatments and prescribed fire in controlling large fire behavior; the role of homeowner practices, such as minimizing vegetation around homes and upgrading building construction materials to prevent house loss; and the relative importance of land planning decisions that could best minimize housing loss while preventing negative impacts to biodiversity.
While the research takes place primarily in southern California, the findings are applicable to other fire-prone non-forested ecosystems such as the Great Basin and the other Mediterranean-climate ecosystems across the world.
The results of this research are shared with management agencies like the National Park Service and U.S. Forest Service, in addition to local and state planners and policy makers, to identify the best strategies to increase community safety while minimizing effects on natural ecosystems.
nflicts between fire management and biodiversity conservation
CBI is collaborating with the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Farm Service Agency to produce an online application depicting ecological and economic features across Bottomland Hardwood Forest Conservation Reserve Program lands in the state of Mississippi. The Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) pays landowners to maintain these Bottomland Hardwood Forests providing important ecological benefits such as removing nitrogen and phosphorus from water, storing flood waters and reducing downstream flooding, trapping sediment, and promoting carbon sequestration. These benefits provided by the CRP are in addition to the restoration and enhancement of wetlands and wildlife habitat. The key ecological and economic features across these CRP lands will be estimated using remote sensing satellite imagery from the Sentinel satellite platform and machine learning modeling using a random forest approach. Additionally CBI staff will be conducting on the ground assessments of the ecological metrics during the 2019 field season.
By providing an online platform that provides metrics on these CRP lands, the USDA Farm Service Agency will be able to better monitor and evaluate existing acres of Bottomland Hardwood Forests that are part of the Conservation Reserve Program. This project is a pilot to determine the utility of the online platform and remote sensing methods, which if proven useful can be expanded to all regions where the CRP restores and enhances Bottomland Hardwood Forests.
The Random Forest modelling process was used to estimate various forest biometric measurements like biomass, density, height, etc., for CRP lands in Mississippi. These were also converted to economic values using standard procedures. We used Forest Inventory and Assessment (FIA) as training data and used field samples to augment the validation of the modelling process. Predicated outputs collected All these outputs were spatialized and incorporated into a customized tool for the USDA Conservation Reserve program.
The CRP tool allows USDA staff, land owners, and third-party organizations to view pertinent spatial information and guide decision making in relation to the status of CRP farms in Mississippi state. This tool allows one to summarize, filter and compare CRP farm tracts across counties and watersheds. You can also download reports in either of two appropriate formats (PDF or CSV). We have also included three different base layers, and relevant contextual data layers that you can view in relation to the CRP farm tracts. You will need permission from USDA to use the tool, but it is available at www.crptool.org. Anyone can view the design of the tool at https://www.sketch.com/s/feba6e2a-ff3e-4c3c-8d2d-9ea4f6bdc896.
CBI initially developed predictive maps of tree height, tree density, biomass, basal area, and forest type using Random Forest machine learning models. Numerous satellite-derived indices from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 sensors, in addition to soils and topography data, were used as predictor inputs. We then refined these predictive models, focusing primarily on biomass improvements, by implementing new methods for processing Sentinel-1 imagery on the cloud computing platform Google Earth Engine (GEE); significantly updating model code; and incorporating preliminary data products derived from NASA’s spaceborne LiDAR mission – the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI). We refined the GEDI LiDAR-derived data products and included them in our models, and overall accuracy for the four forest regression models ranged from 57% to 91%. The Biomass model saw the greatest improvement in accuracy with the R2 increasing by 8%, from 49% to 57%. The Basal Area and Tree Height models both had minor 1-2% increases in accuracy, while the Tree Density model had no improvement. The Forest Type classification model had a negligible improvement in overall accuracy, however, the Elm/Ash/Cottonwood class increased in accuracy by ~6%, from 64% to 70%.
You can get more details in this publication. Degagne, R., Pizzino, D., Friedrich, H, Gough, M., Joseph, G., Iovanna, R., Smith, C. and Strittholt, J. 2022. Mississippi CRP Forest Remote Sensing with Preliminary Global Ecosystem and Dynamics (GEDI) Mission Derived Data Products. CBI Technical Report 2022-1. 40 pp. (10.6084/m9.figshare.19142147)
Wildfires are becoming larger and more severe, causing negative impacts on our natural ecosystems. These post-fire impacts include invasions of exotic plants and an increase in the risk of mudslides, erosion, and siltation of important stream habitat. It is a daunting challenge for resource managers to determine where restoration can do the most good.
In this pilot project, CBI worked with the Santa Barbara Botanic Garden to develop and test online software coupled with a citizen-science process that helps resource managers identify the best candidate locations for restoration in the aftermath of the Thomas and Whittier Fires in Santa Barbara County.
Spatial data about the landscape are combined in a model that provides a preliminary prioritization map, which is then refined using field observations of professionals and community scientists in the Spring following a fire. The sites can then be visited in person to make the final decision about where to focus restoration efforts to maximize the return on the investment.
Figure 1. A flow chart displaying the steps involved in prioritizing areas for post-fire restoration
The community scientists used iNaturalist to record their observations and assist in identifications. You can see the more than 5,000 observations collected so far on iNaturalist here!
How You Can Learn More :
Watch this short video about the project.
View the model with prioritized restoration locations here.
Explore the restoration prioritization map together with other important data layers and photographs in Data Basin.
Read more technical details in this article.
Email john.gallo@consbio.org to be notified of community science opportunities when they arise.



CBI partnered with The Applied Climate Science Lab (ACSL) at the University of Idaho (UI) to expand functionality and data integration between the Northwest Knowledge Network (NKN) and Data Basin. These improvements better enable users to explore and interpret climate-related data, and incorporate that information into their projects and landscape-level or regional planning efforts. Specifically, these improvements allow users to import THREDDS map and data services into Data Basin for visualization. THREDDS is a data hosting system often used for climate-related data.
CBI also created a conterminous US Climate Console that includes simulated climate change impacts on vegetation cover, carbon cycle and fire occurrence and displays both MACA climate projections and MC2 vegetation model results in a web application similar to CBI’s California Climate Console. The Climate Console lowers the barriers to exploring and interpreting climate projections and impacts, and makes this information more readily available for natural resource managers. This tool will enable managers to more easily incorporate near and longer-term climate projections into their resource management planning. It supports making decisions about when to plant restoration species on a site post-fire and areas that are likely to undergo significant longer-term impacts from climate change.
CBI is playing a key role in improving the health and resilience of wetland ecosystems in Southern California in a partnership with the Southern California Wetlands Recovery Project (SCWRP). The newly-released Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool provides data access and decision-support technology for SCWRP’s new Regional Strategy 2018, a recovery plan for tidal and non-tidal wetlands from Point Conception to the Mexican border.
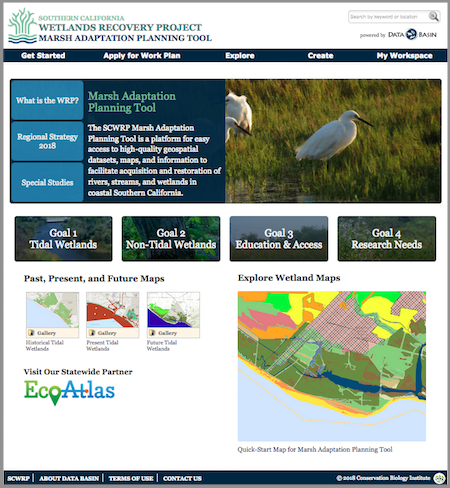
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool homepage, with access to the Regional Strategy 2018, the spatial data that informed its development, and a special tool for planning projects that will contribute to its Work Plan.
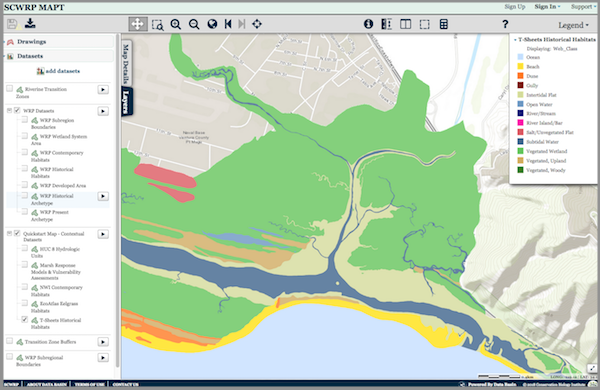
Above: The MAPT’s “Quick-Start Map” that allows the user to explore Southern California’s wetlands. Layers depicting historical and present-day wetlands, important transitions zones, and other features can be turned on and off for quick comparison. The map and its data layers can be downloaded for use in GIS, or saved and used with any other layers in Data Basin.
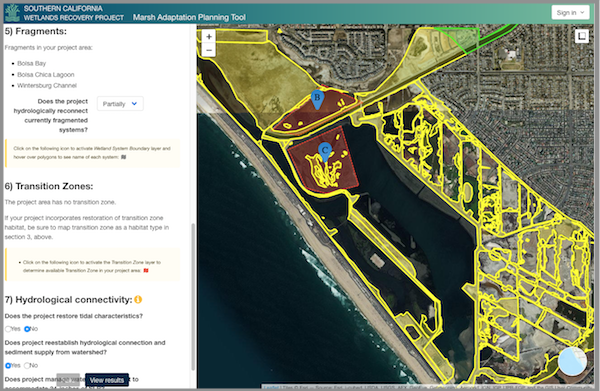
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool’s project planning utility, where project proponents can use Regional Strategy 2018 spatial data, habitat types, and goals and objectives to inform the planning of a project and apply to have it included in the SCWRP Work Plan.
Both land and water resources are essential to agriculture in the San Joaquin Valley and other Mediterranean climates in California. These resources are under pressure from a variety of factors that have the potential to significantly affect the food production capacity of a region that contributes importantly to the food security of the state, nation and the world. The most significant challenges appear to be climate change, especially its impact on water supplies, environmental factors such as in-stream water needs, soil impairment, and urban development.
American Farmland Trust has partnered with the Conservation Biology Institute to undertake a spatial analysis to identify agricultural areas that are most at risk due to these challenges. Understanding how and where water supply shortages, soil impairment, urban growth or climatic changes may impact agriculture will contribute to the discussion of strategies for agricultural adaptation and conservation in the Valley.
This project will build on the successful effort led by CBI to identify areas where large-scale solar energy projects sited in the Valley would pose the least conflict to agricultural and environmental values (A Path Forward). As with the solar project, spatial analysis will occur at a broad Valley wide level, but with a finer grained analysis of at least two counties. A number of scenarios, representing different assumptions about physical and policy trends, will be done to further enrich our understanding of the future prospects of Valley agriculture. Input from technical experts and regional stakeholders will be sought throughout the process to help determine how to rank resource values and risks, and to help formulate future scenarios. We are now actively recruiting stakeholders to participate in the process.
The ultimate goal of the project is to encourage and inform a purposeful regional conversation about strategies that will be needed to meet the land and water resource management challenges and, thus, assure a productive and prosperous future for San Joaquin Valley agriculture.
CBI is producing a spatial decision support system (SDSS) for the Sonoma County Agricultural Preservation and Open Space District (“District”). The District works to conserve habitat, watersheds, and agriculture for people and wildlife in Sonoma County, CA, and is pursuing the development of an SDSS to help guide its land conservation strategies. First, the SDSS will support the development of a ten-year, comprehensive county-wide conservation plan through analysis of multiple conservation themes. It will also assist parcel-scale decisions relating to individual conservation easement projects. In addition, it will produce county-wide outputs (e.g., high priority habitat areas) that can be integrated with other open space planning and scenario-building processes (e.g., the County General Plan). Finally, the SDSS framework—its hierarchical data integration architecture—and supporting data will be published online as an interactive, Web-based program so that the public can explore and learn about the District’s prioritization methods and priority conservation areas.
On the technical end, the Sonoma County SDSS will use an expansion of CBI’s Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (EEMS) along with a new habitat representation algorithm and an expansion of the Linkage Mapper connectivity model (from circuitscape.org). Please contact John Gallo with any questions or comments.
The San Joaquin Valley Data Basin Gateway was created to support a multi-stakeholder effort to identify least conflict lands for utility scale solar development in the San Joaquin Valley in Central California. Stakeholders represented include the solar industry, farming community, ranching community, and environmental community. Each stakeholder group addressed the least conflict question from their perspectives and generated map-based results. After compiling the results, around 470,000 acres of land was identified as potentially desirable to solar developers and least conflict from the standpoint of the other groups. Phase I is complete with a final report due out in February 2016, but the Gateway persists with an extremely valuable data library (~600 datasets pertinent to the region) and other content, and stakeholders have expressed interest in continuing to use the system to continue refining the work into the future.
