CBI has designed and launched a new Data Basin Gateway (Atlas) for the Wildlife Conservation Society Canada focusing on the Yukon Territory to assist WCS Canada researchers and their conservation partners in the region to develop effective protection of wildlife and plants being impacted by a host of environmental stressors, with special emphasis on climate change. In addition to the branded and curated gateway with relevant datasets, we have co-produced a customized application for stakeholders to view and download species distribution models (SDM) for 66 endemic plants designed to predict future changes in their distribution due to climate change. The Atlas houses relevant datasets for conservation planning in the climate-sensitive Yukon region and the tool houses the SDMs, which in combination provide powerful resources for WCS Canada and its partners to effectively plan for resilience.
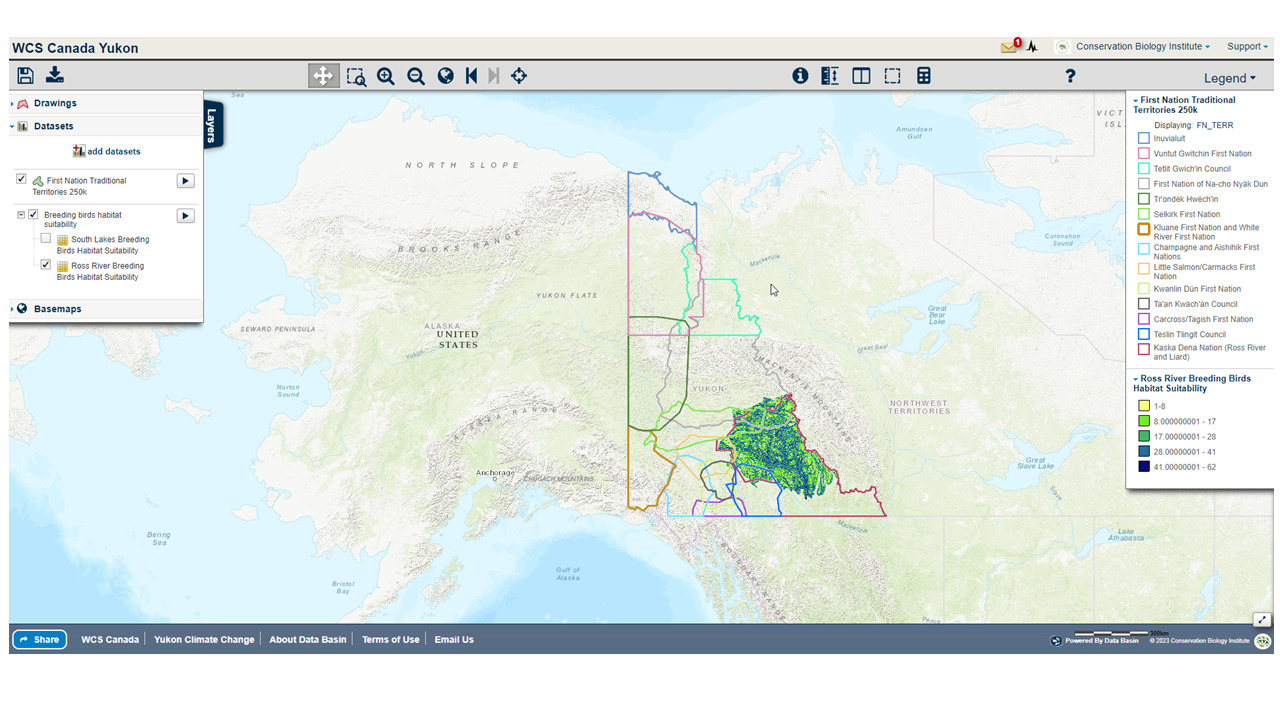
An example of a map created in the WCS Yukon Data Basin Atlas showing First Nation Territories overlaid on Ross river breeding bird habitat suitability layer
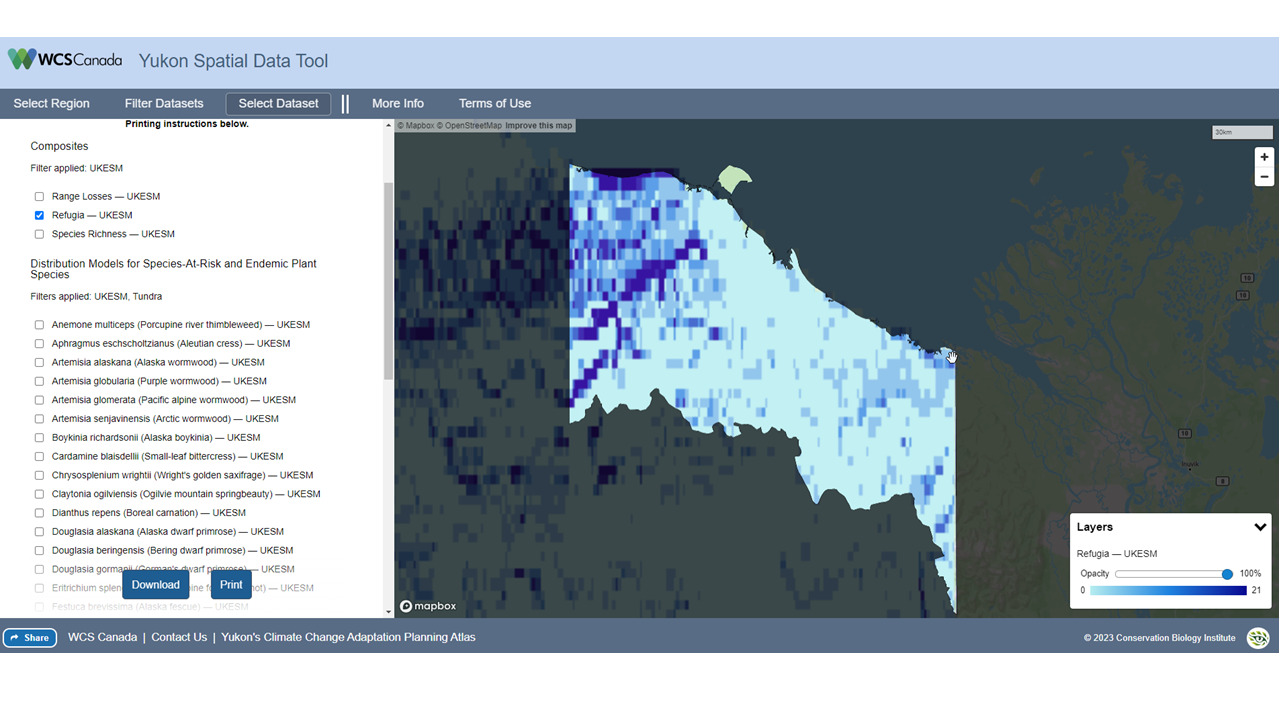
The Yukon Spatial data tool showing projected climate refugia for a Inuvialuit Planning region in the Yukon
Algerian sea lavender (Limonium ramosissimum) and European sea lavender (Limonium duriusculum) are invasive, nonnative perennial plants known to invade salt marsh and upland transitional habitats in coastal California in addition to disturbed inland habitats. While striking in appearance, these two species cause angst among coastal land managers and biologists when detected in salt marsh habitat in San Diego, California. These two species are difficult to eradicate and capable of invading and densely occupying tidal marsh habitat. If left unmanaged these species can displace native vegetation causing loss of breeding and foraging habitat for the endangered Belding’s savannah sparrow (Passerculus sandwichensis beldingi) and extirpating local populations of the endangered salt marsh bird’s beak (Chloropyron maritimum ssp. maritimum).
In 2021, CBI received funding from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service Coastal Program and the San Diego National Wildlife Refuge Complex to determine the distribution of Algerian and European sea lavender and initiate a control program to eliminate these species from San Diego Bay to prevent degradation of salt marsh habitat and potential loss of endangered animal and plant populations. Project partners include the California Department of Parks and Recreation, Port of San Diego, United States Department of the Navy, and the San Diego Bay National Wildlife Refuges.
In August, 2025 CBI was awarded a multi-year award (2025-2028) by the California Wildlife Conservation Board to survey, map, and enhance coastal habitat by controlling these two nonnative species in San Diego Bay in close partnership with multiple agencies and organizations. The management goal is to reduce the distribution of Limonium spp. by 99 percent across approximately 118 acres of mid- to high elevation sale marsh, salt marsh-upland ecotones, and adjacent upland and riparian habitat to benefit 15 rare plants and animals native to the San Diego Bay region.
Conservation Biology Institute is supporting the Spatial Informatics Group – Natural Assets Laboratory (SIG-NAL) on a multi-year Regional Wildlife Mitigation Program (RWMP) in Santa Barbara county that is funded by the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation. Specifically, CBI in partnership with SIG-NAL will develop and propose a fire-resistant buffer or “greenbelt” area in strategic locations within the program area to create wildfire resilient green space, working lands, and habitats. Program outcomes will also provide numerous co-benefits that support watershed and coastal ecological health using a suite of tools including:
- Live oak shaded fuel breaks
- Habitat restoration
- Prescribed herbivory
- Hydrated and agricultural buffers
- Land Conservation
The RWMP is designed to assess hazard, exposure and vulnerability and equitably reduce wildfire hazard across the Santa Barbara front country. The program goals are to decrease the risk of wildfire impacts to structures and infrastructure, promote wildfire resilient green space, working lands, and habitats, and develop community capacity to adapt and recover from the shocks of natural disasters. The Program is divided into three primary Resilience Domains: the Landscape Resilience Domain, the Built Environment Resilience Domain, and the Community Resilient Domain. Each domain will work collaboratively to foster resilience and build adaptive capacity that will allow the community to prepare, respond and recover from the shock of large wildfires. More details can be found at this link: https://rwmpsantabarbara.org/.

Conservation Biology Institute and the Resource Conservation District of the Santa Monica Mountains are working in partnership with local land management agencies and communities to increase wildfire resilience in the Santa Monica Mountains region. The Program has the following tasks:
Raising awareness about wildfire risk in the local communities
- Providing Home Ignition Zone Evaluations to help homeowners reduce their fire risk. If you are interested in having your home evaluated, or getting trained to do evaluations in your neighborhood, contact the RCD SMM.
- Surveying residents about their knowledge of wildfire risk and what they can do to reduce it. Here are the results of the 2021 Survey, and you can take the 2022 Santa Monica Mountains Wildfire Preparedness Survey here.
Helping homeowners prepare for wildfire
- The program provides assistance to homeowners to reduce their wildfire susceptibility by removing hazard trees and restoring burned landscapes to buffer neighborhoods from wildfire
- Learn more about home hardening and ecologically-appropriate defensible space techniques at http://defensiblespace.org.
Mapping and planning the control of flammable invasive weeds in the Woolsey Fire footprint
- The program and its partners Santa Monica Mountains National Recreation Area, Santa Monica Mountains Conservancy, and California State Parks have contracted with Wildlands Conservation Science to conduct aerial surveys to map invasive plant species in the public lands of the Santa Monica Mountains to inform land management to increase future public safety and wildfire preparedness.
- The data and a comprehensive weed control plan will be available by the end of 2023.
Modeling and research to inform planning and decision making
- Program partner U.S. Forest Service Missoula Fire Sciences Lab is modeling ember transport at the property scale under different defensible space conditions. Results of this study will be available in early 2023.
- Conservation Biology Institute conducted ignition and large fire probability modeling to help prioritize locations for risk reduction. See these results here: Wildfire Ignition Potential and Large Wildfire Potential models. You may also see this Wildfire Model Comparison for SMM Region to compare and get access to other important fire risk and hazard maps.
The Santa Monica Mountains Woolsey Fire Recovery and Adaptation Program is funded by the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation.

CBI is supporting the U.S. Forest Service (Region 8) in its efforts toward shared forest stewardship activities. Region 8 contains approximately 244 million acres of forestland, most of which (87%) is privately owned. The Forest Service manages around 5% of the southern forests within 14 National Forests and two Special Units with other public forests make up the remaining 8%. Because of the mixed ownership, close collaboration and shared stewardship is of paramount importance.
CBI has created a customized and curated Data Basin Gateway for the U.S. Forest Service (usfssouth.databasin.org) that supports forest stewardship organizations to access data and information to advance collaborative forest management planning. To demonstrate how to use this framework, a pilot state (North Carolina) was chosen (nc.usfssouth.databasin.org). This gateway uses the “All Lands Strategy” concept to showcase example workflows to facilitate more effective forest management and monitoring across North Carolina. CBI and the North Carolina Shared Stewardship team created supporting training materials is the form of video tutorials and how to materials.
CBI worked closely with the Natural Resource Defense Council (NRDC) to integrate relevant spatial datasets to map areas of high value from the standpoint of carbon storage and sequestration, terrestrial ecological value, and aquatic value in support of several NRDC programs, including their 30X30 campaign to protect 30% of nature in the nation by 2030. Click here to learn more about the 30×30 initiative.
Using CBI’s online modeling software called Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (or EEMS), team members were able to construct, review, and modify the models in a rigorous and highly transparent fashion from their individual remote locations. The resulting “living” models can then be used alone or together and in combination with other spatial data (e.g., existing protected areas) to add further context and insight using Data Basin. Data Basin and EEMS were effectively used to help guide NRDC’s important conservation mission.
In 2006, the Micronesia Challenge began as a commitment by the Republic of Palau, Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Federated State of Micronesia, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands to preserve the marine and terrestrial resources crucial to the survival of the Pacific traditions, cultures, and livelihoods. The overall goal of the initial Micronesia Challenge was to effectively conserve at least 30% of the near-shore marine resources and 20% of the terrestrial resources across Micronesia by 2020.
During the 24th Micronesia Island Forum in 2019, the regional leadership recognized the success of the first 15 years of the Micronesia Challenge and endorsed the new Micronesia Challenge 2030 goals to effectively manage 50% of the marine resources and 30% of terrestrial resources by 2030.
In 2016, the USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) team, regional partners and CBI developed the Micronesia Challenge Regional Terrestrial Monitoring Initiative tool (mcterrestrialmeasures.org) to allow users to visualize the spatial data from the Micronesia Challenge monitoring effort by regional framework indicator(s) that measure the status of managed conservation areas set aside under the program. The first version of the tool included forest data collected between 2003 and 2018 and determined the status and trends in forest area, forest health, understory vegetation, biomass, and carbon storage.
In this new phase of work, the Terrestrial Measure Initiative tool will be updated with the most recent data and information. The team also plans to develop a webinar presentation to communicate with local stakeholders and others about the tool and the ongoing success of the Micronesia Challenge.
The need to plan strategic, effective forest management is urgent in the southern Sierra Nevada, where forests have been ravaged by drought, fire, and catastrophic tree mortality. Multiple, sometimes conflicting, management objectives must be balanced, and multiple agencies need help coordinating their forest restoration actions. A common, readily accessible system evaluating landscape-scale forest condition is needed.
Conservation Biology Institute is working with the Sierra Nevada Conservancy, Sequoia National Forest, Sequoia National Parks, Sequoia Parks Conservancy, Save the Redwoods League, and others to develop forest resilience models and create a toolkit for exploring these data to support the planning of a range of resource management goals. These goals include the protection of sequoia groves, overall forest health, wildfire protection, and endangered species habitat management. The project is supported by CBI’s data sharing and mapping platform Data Basin. The project is funded by the Save the Redwood League and Sequoia National Park through its partner the Sequoia Parks Conservancy, and CAL FIRE Forest Health Research Grant Program.
Cachuma Resource Conservation District (RCD) is working in partnership with Conservation Biology Institute, LegacyWorks, and Sharyn Main Consulting on the Regional Priority Plan to Reduce Wildfire Risk and Improve Forest Health in Santa Barbara County (RPP), which is a flagship project of the Santa Barbara County Conservation Blueprint. Funded by the California Coastal Conservancy, the RPP helps with the planning, mapping, and prioritization of projects that will proactively address wildfire threat in Santa Barbara County, as well as improve forest and habitat health.
The RPP is a multi-prong collaboration, which focuses on public and private land in the wildland/urban interface (WUI). CBI is the lead for a component of the project, to develop a sophisticated decision-support mapping tool to not only predict areas of high fire-risk on a landscape scale, but also help the community prioritize where fire risk mitigation projects should occur. The tool will serve as a community resource within the Santa Barbara County Conservation Blueprint and should improve communication, network building, and support community priorities through a regional approach to fire resilience and habitat health. The project team is talking with the many agencies and stakeholders involved, and facilitating the collaborative decision-making process.
CBI recently worked with the Pacific Marine & Estuarine Fish Habitat Partnership (PMEP) to update the West Coast Estuaries Explorer, a tool designed to engage a broad range of users with detailed information about estuaries along the U.S. West Coast. The first version of this tool was developed in partnership with PMEP and the North Pacific Landscape Conservation Cooperative. The partnership between CBI and PMEP continues with support from NOAA and the Pacific States Marine Fisheries Commission (PSMFC). The Estuaries Explorer got several performance and design updates to make it easier to use and more visually engaging. In addition to the latest available information for estuary boundaries and biological habitats, the Explorer now includes aerial images for each of the estuaries in Washington, Oregon, and California. Later this year, CBI and PMEP will incorporate additional information on the location of eelgrass habitat and areas of tidal wetland loss. PSMFC has taken over long-term hosting of this exciting tool.
