In this project, CBI is a member of and also providing support to the Fort Bragg Headlands Consortium, with a mission to to help achieve environmentally sound restoration and development solutions that will improve the quality of life and economy for current and future residents of our Coast.
CBI’s major contribution to the Consortium is to develop and maintain the Fort Bragg Headlands web-mapping Gallery. Powered by Data Basin, this web-mapping Gallery is a feature-rich platform for local citizens, stakeholders and decision-makers to access publicly available spatial data (e.g. maps of streams, wetlands, hazards, soils, geology, etc.). This is timely, as Fort Bragg is currently making a significant Local Coastal Program (LCP) Amendment. Currently zoned Forest Light Industrial, these zoning changes will make the third of the city that was once a lumber mill into prime real estate zoned for profitable development. Fort Bragg is also figuring out how to deal with the remaining wetlands out there that still contain hazardous materials despite a first round of clean-up by the landowner. Providing easy access to data and maps will facilitate decisions that conserve the landscapes and biodiversity of the Fort Bragg region while bringing much needed development and jobs to sustain current and future generations. You can donate directly to this cause here.
Wildfires are a natural part of California ecosystems and play an important role in maintaining ecological structure and function. However, different fire regimes in the state have been altered due to past management practices, climate change, invasive species, and population growth and urban expansion. Given the potential for conflicts between fire management and conserving biodiversity and ecological functioning, solutions are needed to balance ecosystem health with human welfare and community safety.
CBI is partnering with Dr. Jon Keeley (USGS) and an international team of landscape ecologists, biologists, geographers and economists to study the factors that control wildfire activity in southern California, which experiences the largest number of housing losses to wildfire in the U.S. This work focuses on the role of different ignition sources, climate patterns, vegetation change, and housing location and arrangement in altering fire patterns and contributing to housing loss at the wildland-urban interface. Other topics of research include the effectiveness and effects of fuel treatments and prescribed fire in controlling large fire behavior; the role of homeowner practices, such as minimizing vegetation around homes and upgrading building construction materials to prevent house loss; and the relative importance of land planning decisions that could best minimize housing loss while preventing negative impacts to biodiversity.
While the research takes place primarily in southern California, the findings are applicable to other fire-prone non-forested ecosystems such as the Great Basin and the other Mediterranean-climate ecosystems across the world.
The results of this research are shared with management agencies like the National Park Service and U.S. Forest Service, in addition to local and state planners and policy makers, to identify the best strategies to increase community safety while minimizing effects on natural ecosystems.
nflicts between fire management and biodiversity conservation
Destructive wildfires are sudden, extreme events: In a matter of hours, both social and ecological communities are transformed by the loss of homes and lives, and change in natural vegetation. After such an event, residents take stock of their transformed landscape and environment, deciding to remain, rebuild, or move, while ecological communities restructure and regrow. These combined social and ecological responses to wildfire may present a ‘hot moment’ or ‘window of opportunity’ where governments, communities, and residents can take action to reduce the future exposure to disaster.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers, convened by CBI’s Dr. Alexandra Syphard, Dr. Miranda Mockrin from Northern Research Station, USDA Forest Service and Dr. Van Butsic, from the Department of Environmental Science, Policy, & Management at University of California, Berkeley, are examining the question “Do wildfires lead to transformative adaptation, reducing future wildfire risk or do they lead to entrenchment, as residents and institutions re-create hazard-prone environments?”
To examine this question, they will review national data of post-fire housing change (rebuilding, sales, new development, land subdivision) and investigate how social and ecological settings and impacts, as well as event characteristics, influence subsequent housing and ecological trends. They will also determine, at the household scale, how changes in housing patterns relate to the post-wildfire ecological setting and socioeconomic characteristics, determining adaptation or entrenchment.
Wildfire is an important ecological process in California, where a diversity of fire regimes shape the structure and composition of plant and animal communities. Fire regimes are changing beyond their historical range of variability, however, due to several factors, including past fire management, invasive species, land use change, and climate change. These changes not only threaten the integrity and diversity of biological communities, but affect human communities, too, as residential losses to wildfire have skyrocketed in the last several decades. Two of these drivers, land use and climate, are expected to change dramatically in the coming century, raising substantial concern about their effects on fire regimes and subsequent impacts to human communities and biological diversity.
CBI has partnered with University of California, Berkeley to develop and implement a scenario-based integrated modeling framework to quantify the relative importance of climatic and land use factors on current and future projected fire patterns and risk of structure loss for three study areas in California. Select research questions driving this project include:
1) How do patterns of fire activity vary by land use change and climate?
2) How does structure loss vary by land use and climate change?
3) How do these relationships varyby geographic region?
4) Given these relationships, how are large fires and associated structure risk likely to change in the future?
Results of the assembled model output will be distributed to appropriate stakeholders and Data Basin will host the mapped output data.


CBI will use the San Diego Monitoring and Management Program’s Inspect and Manage rare plant monitoring protocol to document rare plant species population size, spatial extent, and threats and will make management recommendations based on the identified threats. The Cooperative Agreement has the potential to extend through 2023 and supports several objectives listed in the Naval Base Point Loma and Naval Base Coronado’s Integrated Natural Resources Plan.
Working with Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, Oregon Department of Transportation, US Fish and Wildlife Service, and other governmental and non-governmental partners, CBI is reviewing the current state of knowledge and is developing a wildlife and habitat connectivity blueprint for the State of Oregon, including the plan for generating a number of useful map-based products and online tools that will address planning at multiple scales across the state. This initial phase is expected to conclude in January 2018 with testing of the blueprint being carried out for a subset of the state (Coast Range and Klamath ecoregions) through different funding.
The Conservation Biology Institute will partner with The US Fish and Wildlife Service, Refuges Lands Division and North Pacific LCC, to develop an interactive web-based mapping tool to support the Willamette Valley Conservation Study (WVCS). This tool will be targeted to conservation partners in the region, as well as the general public. The primary objective of this web-mapping tool is to serve as a communication and data exploration tool for priority areas identified within the WVCS, and will allow users to understand the key characteristics of each priority area and better understand why each area was selected.
This tool will be developed and managed by CBI, alongside and embedded in the North Pacific LCC’s Conservation Planning Atlas (http://wvcs.apps.nplcc.databasin.org/).
CBI is playing a key role in improving the health and resilience of wetland ecosystems in Southern California in a partnership with the Southern California Wetlands Recovery Project (SCWRP). The newly-released Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool provides data access and decision-support technology for SCWRP’s new Regional Strategy 2018, a recovery plan for tidal and non-tidal wetlands from Point Conception to the Mexican border.
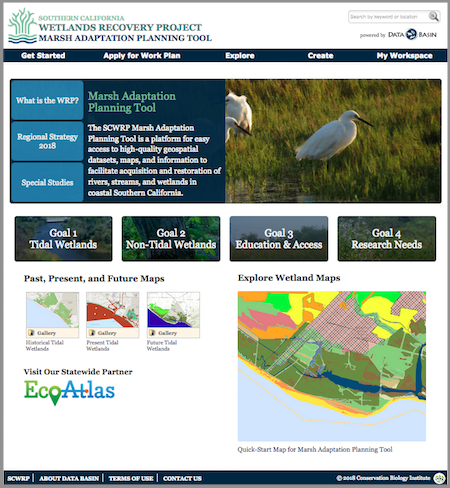
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool homepage, with access to the Regional Strategy 2018, the spatial data that informed its development, and a special tool for planning projects that will contribute to its Work Plan.
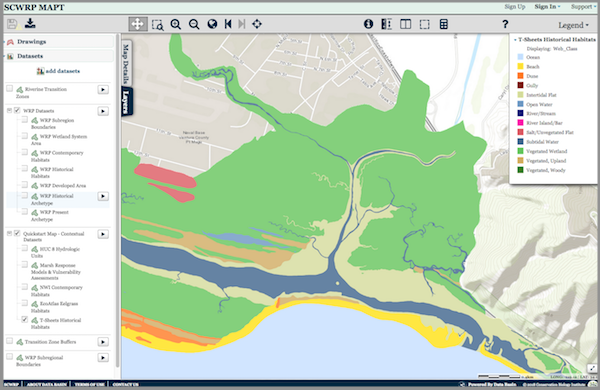
Above: The MAPT’s “Quick-Start Map” that allows the user to explore Southern California’s wetlands. Layers depicting historical and present-day wetlands, important transitions zones, and other features can be turned on and off for quick comparison. The map and its data layers can be downloaded for use in GIS, or saved and used with any other layers in Data Basin.
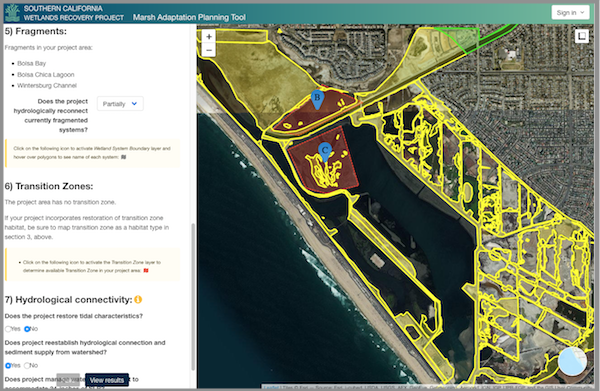
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool’s project planning utility, where project proponents can use Regional Strategy 2018 spatial data, habitat types, and goals and objectives to inform the planning of a project and apply to have it included in the SCWRP Work Plan.
The Micronesia Challenge is a commitment by the Republic of Palau, Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Federated State of Micronesia, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands to preserve the marine and terrestrial resources that are crucial to the survival of the Pacific traditions, cultures and livelihoods. The overall goal of the Micronesia Challenge is to effectively conserve at least 30% of the near-shore marine resources and 20% of the terrestrial resources across Micronesia by 2020. The USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) team, regional partners and CBI developed the Micronesia Challenge Regional Terrestrial Monitoring Initiative tool (mcterrestrialmeasures.org) to allow users to visualize the spatial data from the Micronesia Challenge monitoring effort by regional framework indicator(s) that measure the status of managed conservation areas set aside under the program. Forest data were collected between 2003 and 2018 and are now being used to determine the status and trends in forest area, forest health, understory vegetation, biomass, and carbon storage.
