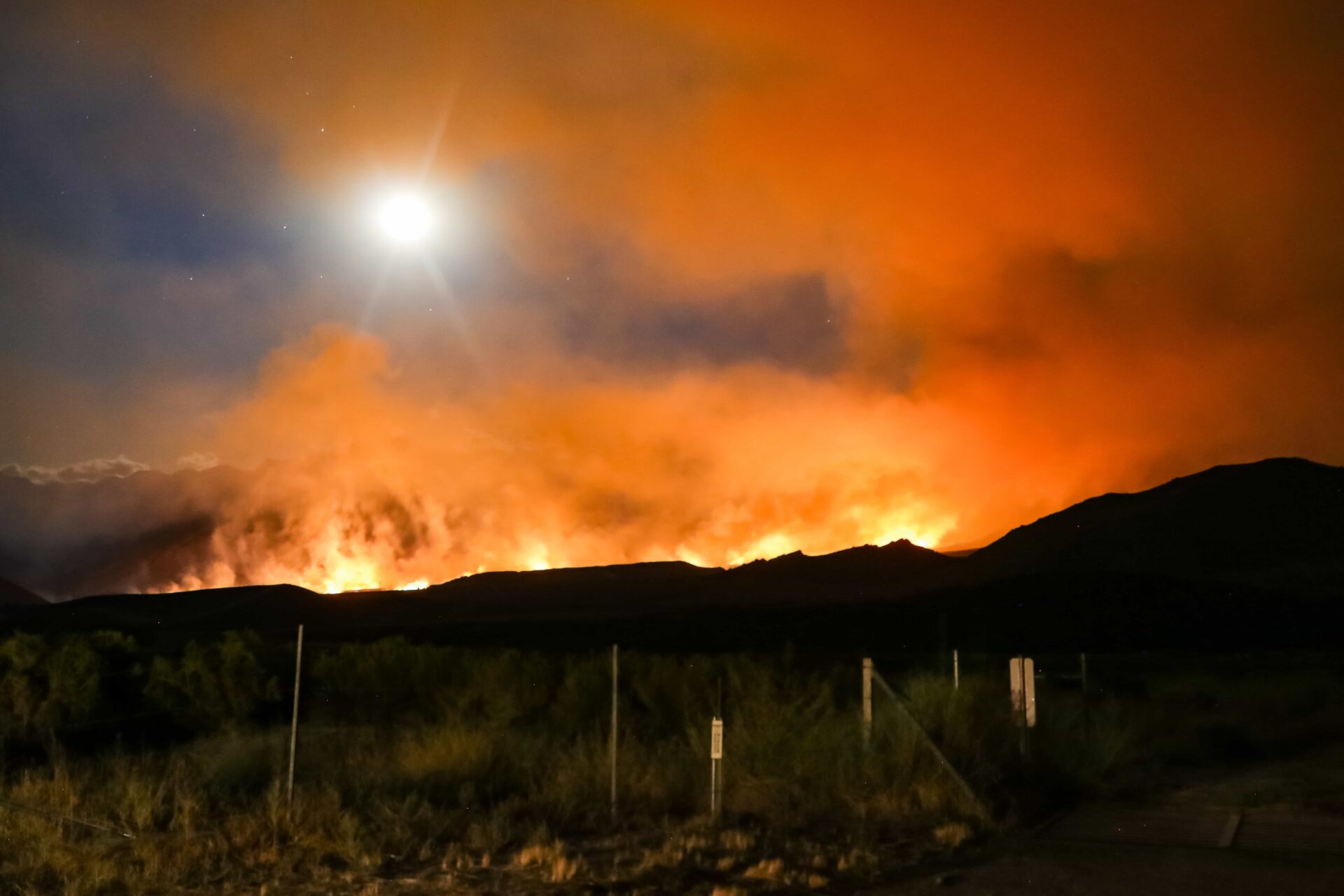
Destructive wildfires are sudden, extreme events: In a matter of hours, both social and ecological communities are transformed by the loss of homes and lives, and change in natural vegetation. After such an event, residents take stock of their transformed landscape and environment, deciding to remain, rebuild, or move, while ecological communities restructure and regrow. These combined social and ecological responses to wildfire may present a ‘hot moment’ or ‘window of opportunity’ where governments, communities, and residents can take action to reduce the future exposure to disaster.
An interdisciplinary team of researchers, convened by CBI’s Dr. Alexandra Syphard, Dr. Miranda Mockrin from Northern Research Station, USDA Forest Service and Dr. Van Butsic, from the Department of Environmental Science, Policy, & Management at University of California, Berkeley, are examining the question “Do wildfires lead to transformative adaptation, reducing future wildfire risk or do they lead to entrenchment, as residents and institutions re-create hazard-prone environments?”
To examine this question, they will review national data of post-fire housing change (rebuilding, sales, new development, land subdivision) and investigate how social and ecological settings and impacts, as well as event characteristics, influence subsequent housing and ecological trends. They will also determine, at the household scale, how changes in housing patterns relate to the post-wildfire ecological setting and socioeconomic characteristics, determining adaptation or entrenchment.
Wildfire is an important ecological process in California, where a diversity of fire regimes shape the structure and composition of plant and animal communities. Fire regimes are changing beyond their historical range of variability, however, due to several factors, including past fire management, invasive species, land use change, and climate change. These changes not only threaten the integrity and diversity of biological communities, but affect human communities, too, as residential losses to wildfire have skyrocketed in the last several decades. Two of these drivers, land use and climate, are expected to change dramatically in the coming century, raising substantial concern about their effects on fire regimes and subsequent impacts to human communities and biological diversity.
CBI has partnered with University of California, Berkeley to develop and implement a scenario-based integrated modeling framework to quantify the relative importance of climatic and land use factors on current and future projected fire patterns and risk of structure loss for three study areas in California. Select research questions driving this project include:
1) How do patterns of fire activity vary by land use change and climate?
2) How does structure loss vary by land use and climate change?
3) How do these relationships varyby geographic region?
4) Given these relationships, how are large fires and associated structure risk likely to change in the future?
Results of the assembled model output will be distributed to appropriate stakeholders and Data Basin will host the mapped output data.


CBI will use the San Diego Monitoring and Management Program’s Inspect and Manage rare plant monitoring protocol to document rare plant species population size, spatial extent, and threats and will make management recommendations based on the identified threats. The Cooperative Agreement has the potential to extend through 2023 and supports several objectives listed in the Naval Base Point Loma and Naval Base Coronado’s Integrated Natural Resources Plan.
CBI is collaborating with the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Farm Service Agency to produce an online application depicting ecological and economic features across Bottomland Hardwood Forest Conservation Reserve Program lands in the state of Mississippi. The Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) pays landowners to maintain these Bottomland Hardwood Forests providing important ecological benefits such as removing nitrogen and phosphorus from water, storing flood waters and reducing downstream flooding, trapping sediment, and promoting carbon sequestration. These benefits provided by the CRP are in addition to the restoration and enhancement of wetlands and wildlife habitat. The key ecological and economic features across these CRP lands will be estimated using remote sensing satellite imagery from the Sentinel satellite platform and machine learning modeling using a random forest approach. Additionally CBI staff will be conducting on the ground assessments of the ecological metrics during the 2019 field season.
By providing an online platform that provides metrics on these CRP lands, the USDA Farm Service Agency will be able to better monitor and evaluate existing acres of Bottomland Hardwood Forests that are part of the Conservation Reserve Program. This project is a pilot to determine the utility of the online platform and remote sensing methods, which if proven useful can be expanded to all regions where the CRP restores and enhances Bottomland Hardwood Forests.
The Random Forest modelling process was used to estimate various forest biometric measurements like biomass, density, height, etc., for CRP lands in Mississippi. These were also converted to economic values using standard procedures. We used Forest Inventory and Assessment (FIA) as training data and used field samples to augment the validation of the modelling process. Predicated outputs collected All these outputs were spatialized and incorporated into a customized tool for the USDA Conservation Reserve program.
The CRP tool allows USDA staff, land owners, and third-party organizations to view pertinent spatial information and guide decision making in relation to the status of CRP farms in Mississippi state. This tool allows one to summarize, filter and compare CRP farm tracts across counties and watersheds. You can also download reports in either of two appropriate formats (PDF or CSV). We have also included three different base layers, and relevant contextual data layers that you can view in relation to the CRP farm tracts. You will need permission from USDA to use the tool, but it is available at www.crptool.org. Anyone can view the design of the tool at https://www.sketch.com/s/feba6e2a-ff3e-4c3c-8d2d-9ea4f6bdc896.
CBI initially developed predictive maps of tree height, tree density, biomass, basal area, and forest type using Random Forest machine learning models. Numerous satellite-derived indices from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 sensors, in addition to soils and topography data, were used as predictor inputs. We then refined these predictive models, focusing primarily on biomass improvements, by implementing new methods for processing Sentinel-1 imagery on the cloud computing platform Google Earth Engine (GEE); significantly updating model code; and incorporating preliminary data products derived from NASA’s spaceborne LiDAR mission – the Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI). We refined the GEDI LiDAR-derived data products and included them in our models, and overall accuracy for the four forest regression models ranged from 57% to 91%. The Biomass model saw the greatest improvement in accuracy with the R2 increasing by 8%, from 49% to 57%. The Basal Area and Tree Height models both had minor 1-2% increases in accuracy, while the Tree Density model had no improvement. The Forest Type classification model had a negligible improvement in overall accuracy, however, the Elm/Ash/Cottonwood class increased in accuracy by ~6%, from 64% to 70%.
You can get more details in this publication. Degagne, R., Pizzino, D., Friedrich, H, Gough, M., Joseph, G., Iovanna, R., Smith, C. and Strittholt, J. 2022. Mississippi CRP Forest Remote Sensing with Preliminary Global Ecosystem and Dynamics (GEDI) Mission Derived Data Products. CBI Technical Report 2022-1. 40 pp. (10.6084/m9.figshare.19142147)
Wildfires are becoming larger and more severe, causing negative impacts on our natural ecosystems. These post-fire impacts include invasions of exotic plants and an increase in the risk of mudslides, erosion, and siltation of important stream habitat. It is a daunting challenge for resource managers to determine where restoration can do the most good.
In this pilot project, CBI worked with the Santa Barbara Botanic Garden to develop and test online software coupled with a citizen-science process that helps resource managers identify the best candidate locations for restoration in the aftermath of the Thomas and Whittier Fires in Santa Barbara County.
Spatial data about the landscape are combined in a model that provides a preliminary prioritization map, which is then refined using field observations of professionals and community scientists in the Spring following a fire. The sites can then be visited in person to make the final decision about where to focus restoration efforts to maximize the return on the investment.
Figure 1. A flow chart displaying the steps involved in prioritizing areas for post-fire restoration
The community scientists used iNaturalist to record their observations and assist in identifications. You can see the more than 5,000 observations collected so far on iNaturalist here!
How You Can Learn More :
Watch this short video about the project.
View the model with prioritized restoration locations here.
Explore the restoration prioritization map together with other important data layers and photographs in Data Basin.
Read more technical details in this article.
Email john.gallo@consbio.org to be notified of community science opportunities when they arise.



The Stephens’ kangaroo rat (Dipodomys stephensi) is an endangered mammal of grassland habitats in southern California. CBI is helping to conserve the species using satellite technology and advanced mapping techniques.
Kangaroo rats (or Krats, as biologists often call them) are seed-eating rodents restricted to arid regions of southwestern North America. The 20 or so Krat species are biologically similar to jerboas of the Mideast–and like mideastern jerboas and the kangaroos of Australia, they use their large hind limbs to bound efficiently and elusively through open habitats, especially deserts and grasslands. Being mostly nocturnal, Krats also have huge eyes for night vision and keen ears for hearing predators, like owls and foxes.
Stephens’ kangaroo rat (or biological shorthand, SKR) occupies open, undeveloped grasslands in western Riverside and San Diego counties in southern California. Because much of their habitat has been paved over and fragmented by development, the SKR was listed as Endangered under the the US Endangered Species Act and Threatened under the California ESA in the 1980s. Numerous ecological reserves have since been established to conserve remaining populations. Unfortunately, these scattered Krat reserves are not consistently managed, monitored, or even understood by the responsible resource management agencies, largely because it is difficult to map and track suitable habitat conditions over space and time. Traditional habitat variables, such as vegetation and soil types, are not nuanced enough to reflect the on-ground conditions that SKR need, and management and monitoring approaches differ amongst the reserves.
CBI is helping remedy this situation by using satellite imagery and innovative habitat modeling techniques to develop reliable statistical models to map habitat suitability across the species’ geographic range. In partnership with the US Fish and Wildlife Service, the Riverside County Habitat Conservation Agency (RCHCA), and species experts, we are developing a coordinated approach to mapping SKR habitat suitability to manage and monitor the species in a more scientifically consistent and justified manner. Specifically, we are using European Sentinel-2 satellite imagery, in concert with other reliable geographic data, to develop habitat suitability maps that can be routinely updated over time across the species range as conditions change. The resulting models will be used to inform management and monitoring efforts to conserve and recover this charismatic endangered species.
CBI is collaborating with the Rogue River-Siskiyou National Forest and the Klamath National Forest in their effort to conserve the Alaska yellow Cedar in its southern range, located in Southern Oregon and Northern California, where it faces extreme extinction risk due to climate change. Concerted conservation efforts are needed to develop and implement conservation and reforestation strategies, in order to manage forest tree species for sustainability in the future. CBI will help coordinate the collection of seeds from trees from 8 sites, tag and geo-reference each tree, gather information on the general health of these stands, and submit the seeds to the national seedbank in Fort Collins. In addition, current-year needles will be also collected from each seed tree for later genetic/genomics analysis by Richard Cronn and team at the Pacific Northwest Research Station of the USFS.
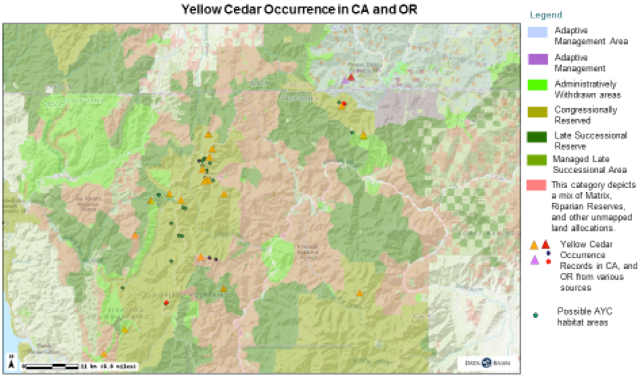
Alaska Yellow Cedar (Callitropsis nootkatensis) has an extensive range from Alaska to Northern California (Fig. 1). It is declining in the northern part of its range due to a combination of factors associated with climate change and is a rare species in the southern part of its range in California and Southern Oregon. These southern populations are relics that occur in isolated stands in sub-alpine zones in cool wet sites at higher elevation > 5000 ft (Fig 2). The species is currently under review for listing as a threatened or endangered species.
Update 12/18
CBI finished cone collections in September, 2018, from six populations across three sites in Southern Oregon and three sites in Northern California. Access to other sites was restricted due to the Klondike Fire burning in Southern Oregon. This completes the first systematic collection of mature cones from these southern populations.
We have recieved word from the US Forest Service, Bend Seed Extractory, located in Bend Oregon, that they have successfully extracted viable seeds. The next step is to send them to the National Seed Laboratory in Dry Branch, Georgia, USA. Once there, these seeds will be entered into the the national germplasm bank making these the very first entries for these relic southern populations.
Needle tissue that was collected from 10 trees at each site will be genetically analyzed by researchers at the USFS Forest Science lab in Corvallis.This analysis will help determine if these populations are genetically distinct sub-populations from their northern counterparts which will help guide conservation of this species.
The Rogue River-Siskiyou National forest office is planning to use some of these seeds to grow seedlings to test for certain traits such as disease resistance and drought tolerance. The hope is that seeds collected from these southern populations may be used for restoration plantings in the northern regions.
In the north, Alaska Yellow Cedar is a valuable timber species but has been declining as a result of the climate crisis.
Conservation of these southern populations may prove to be critical for the longterm management of northern Alaska Yellow Cedars on public and private lands.
Fig 1. Range map for Alaska yellow cedar.
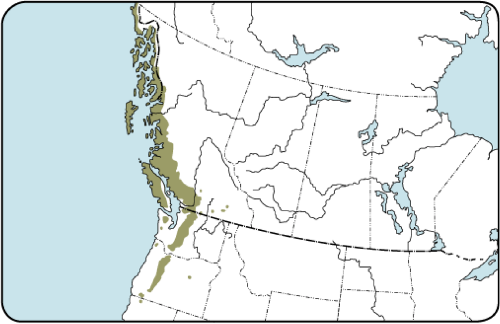
Source: http://tidcf.nrcan.gc.ca/en/trees/factsheet/376
Figure 2. Current known yellow cedar locations in the Siskyou Mountains (CBI 2017)
Primary forests make up approximately one-third of the world’s remaining forests. Globally, they are grossly under-represented in protected areas and subject to industrial-scale logging and “sustainable forest management” that otherwise fragment intact areas. They face unprecedented threats from logging, mining, energy development, and climate change. British Columbia contains two globally important temperate rainforests with substantial primary and intact forest landscapes distributed from the coast (i.e. Great Bear Rainforest – GBR) inland (i.e., Inland Rainforest). Geos Institute proposes to map and assess conservation importance of the primary forests in these regions as a scientific basis for an international campaign aimed at protecting these globally important rainforests. CBI will support Geos Institute and partners in Canada to help map the area accurately, provide scientific input, and also do a carbon flux model for these primary rainforests.
