CBI is supporting the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) in its work to develop a strategic, comprehensive approach for conducting inventory, monitoring, and assessments that respond to the priorities of the whole agency instead of individual or programmatic needs. Many of today’s management decisions require a landscape approach to acquiring and analyzing information about forests and rangelands. Therefore an effective inventory, monitoring and assessment system requires working across organizational boundaries to determine common goals, avoid duplication and build on common information needs. CBI will provide support to assess existing data collection, management and storage methods for the USFS Region 8 and make recommendations regarding the relationship agency data has with current decision support processes.
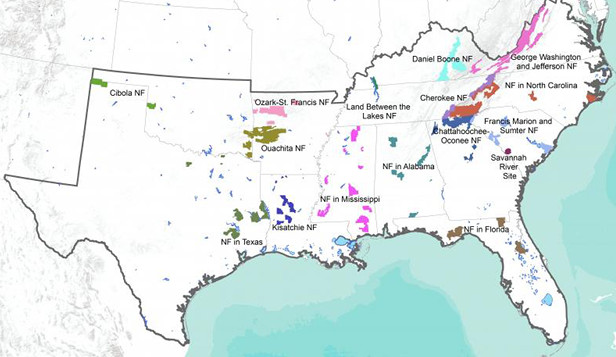
While the U.S. Forest Service National Forest Review projects are focused at the individual Forest level, the Census of Inventory, Monitoring, and Assessment Activities is focused on Region 8, which encompasses 15 Forests and covers 13 states in the southeastern United States.
Both land and water resources are essential to agriculture in the San Joaquin Valley and other Mediterranean climates in California. These resources are under pressure from a variety of factors that have the potential to significantly affect the food production capacity of a region that contributes importantly to the food security of the state, nation and the world. The most significant challenges appear to be climate change, especially its impact on water supplies, environmental factors such as in-stream water needs, soil impairment, and urban development.
American Farmland Trust has partnered with the Conservation Biology Institute to undertake a spatial analysis to identify agricultural areas that are most at risk due to these challenges. Understanding how and where water supply shortages, soil impairment, urban growth or climatic changes may impact agriculture will contribute to the discussion of strategies for agricultural adaptation and conservation in the Valley.
This project will build on the successful effort led by CBI to identify areas where large-scale solar energy projects sited in the Valley would pose the least conflict to agricultural and environmental values (A Path Forward). As with the solar project, spatial analysis will occur at a broad Valley wide level, but with a finer grained analysis of at least two counties. A number of scenarios, representing different assumptions about physical and policy trends, will be done to further enrich our understanding of the future prospects of Valley agriculture. Input from technical experts and regional stakeholders will be sought throughout the process to help determine how to rank resource values and risks, and to help formulate future scenarios. We are now actively recruiting stakeholders to participate in the process.
The ultimate goal of the project is to encourage and inform a purposeful regional conversation about strategies that will be needed to meet the land and water resource management challenges and, thus, assure a productive and prosperous future for San Joaquin Valley agriculture.
CBI is assisting the US Forest Service, Region 1, with reconciling habitat conservation efforts with long-term forest resiliency planning in the northern Rocky Mountains. Partners include the Southwest Crown Collaborative, Montana State University, and the USFS Rocky Mountain Research Station. Conceptual deliverables include a framework for integrating the habitat requirements of threatened species into a forest restoration plan that recognizes the dynamic nature of forest ecosystems and the importance of large-scale ecological processes. More definitive deliverables include an analysis of how habitat composition and configuration has changed over the past 90 to 100 years, a plan for restoring the dynamic nature of forests at the watershed scale, and analytical tools to facilitate similar efforts in other areas.
This effort reflects CBI’s commitment to assisting in the restoration of western public lands, recognizing the importance of promoting resilient forests in the face of a changing climate, and the conservation of native biodiversity. Future implications would include helping federal agencies such as the Forest Service transition into an analytical model that views habitat as a critical but dynamic component of forest planning, one the requires intact, large-scale ecological processes for long-term maintenance.
Supported by the California Wildlife Conservation Board, CBI will be working closely with the Strategic Growth Council, UC Davis, and other agency staff to conduct a Regional Conservation Assessment (RCA) for two pilot areas in the state – Mojave Desert and Modoc Plateau – and build an easy-to-use, online assessment tool to evaluate potential conservation investments based on a set of standards developed by the Integrated Regional Conservation and Development program (IRCAD). RCAs are designed to provide a standardized and current assessment of the biological values and ecological conditions within each ecoregion in California serving as the important context to carry out more effective and ecologically sensitive development in the state. This project builds upon existing investment through the California Energy Commission’s statewide renewable energy planning efforts.
The Coyote Valley is a last chance landscape. The Valley, located within one of the world’s top 25 most important biodiversity hotspots, occurs on the south side of San Jose, California and is situated between the Santa Cruz Mountains and Diablo Range. The Santa Clara Valley Open Space Authority, in partnership with CBI, assembled a team of local and regional scientists with the goal of integrating existing scientific information and knowledge to develop a vision and practical plan for achieving a fully functional landscape linkage through the Valley to avoid isolating the two mountain ranges while protecting extremely important valley floor species and habitats. The plan includes restoration of important wetland and uplands habitats, support for numerous rare and sensitive species, and protection of important water and agricultural resources.
*Click here for the full report.
A Regional Conservation Investment Strategy (RCIS) is a voluntary, non-regulatory, and non-binding conservation assessment that includes information and analyses relating to the conservation of focal species, their associated habitats, and the conservation status of the RCIS land base. The RCIS program, which is administered by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife, was created by state bill AB 2087. This conservation strategy is intended to guide conservation investments and advance mitigation in RCIS areas. CBI provided scientific and technical support to ICF International, who led the development of a pilot RCIS for the Antelope Valley in LA County. Implementation of this strategy is intended to sustain and enhance focal species and their habitats in the face of climate change and other stressors such as habitat loss and fragmentation.
Working with Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, Oregon Department of Transportation, US Fish and Wildlife Service, and other governmental and non-governmental partners, CBI is reviewing the current state of knowledge and is developing a wildlife and habitat connectivity blueprint for the State of Oregon, including the plan for generating a number of useful map-based products and online tools that will address planning at multiple scales across the state. This initial phase is expected to conclude in January 2018 with testing of the blueprint being carried out for a subset of the state (Coast Range and Klamath ecoregions) through different funding.
CBI is playing a key role in improving the health and resilience of wetland ecosystems in Southern California in a partnership with the Southern California Wetlands Recovery Project (SCWRP). The newly-released Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool provides data access and decision-support technology for SCWRP’s new Regional Strategy 2018, a recovery plan for tidal and non-tidal wetlands from Point Conception to the Mexican border.
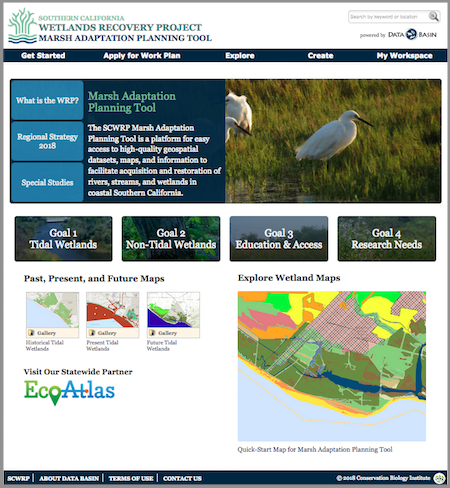
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool homepage, with access to the Regional Strategy 2018, the spatial data that informed its development, and a special tool for planning projects that will contribute to its Work Plan.
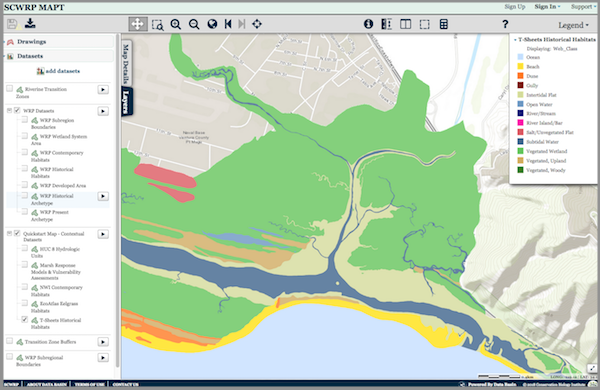
Above: The MAPT’s “Quick-Start Map” that allows the user to explore Southern California’s wetlands. Layers depicting historical and present-day wetlands, important transitions zones, and other features can be turned on and off for quick comparison. The map and its data layers can be downloaded for use in GIS, or saved and used with any other layers in Data Basin.
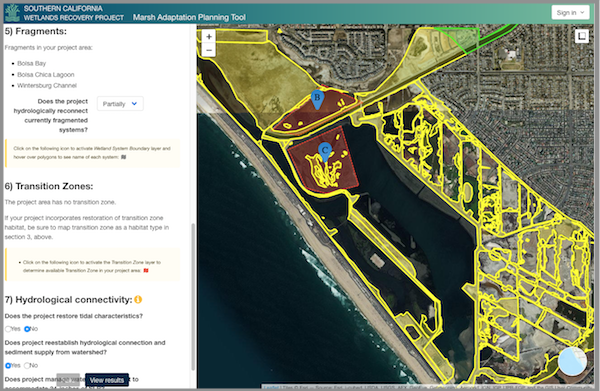
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool’s project planning utility, where project proponents can use Regional Strategy 2018 spatial data, habitat types, and goals and objectives to inform the planning of a project and apply to have it included in the SCWRP Work Plan.
The Micronesia Challenge is a commitment by the Republic of Palau, Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, the Federated State of Micronesia, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands to preserve the marine and terrestrial resources that are crucial to the survival of the Pacific traditions, cultures and livelihoods. The overall goal of the Micronesia Challenge is to effectively conserve at least 30% of the near-shore marine resources and 20% of the terrestrial resources across Micronesia by 2020. The USFS Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) team, regional partners and CBI developed the Micronesia Challenge Regional Terrestrial Monitoring Initiative tool (mcterrestrialmeasures.org) to allow users to visualize the spatial data from the Micronesia Challenge monitoring effort by regional framework indicator(s) that measure the status of managed conservation areas set aside under the program. Forest data were collected between 2003 and 2018 and are now being used to determine the status and trends in forest area, forest health, understory vegetation, biomass, and carbon storage.
