CBI has partnered with the Paulson Institute (PI), the Foreign Economic Cooperation Office (FECO) of the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China (MEP), and the State of California to provide FECO with an Environmental Risk Screening Tool that will help guide Chinese international investment projects. The overarching goal of the tool is to significantly reduce negative environmental impacts as the result of Chinese development projects around the world.
The screening tool will include interactive mapping of biodiversity and environmental data against which potential development projects can be evaluated. The tool will include a standard Biodiversity Impact Analysis using a set of internationally recognized datasets (e.g., Key Biodiversity Areas, Critical Natural Habitat, Alliance for Zero Extinction sites, and Protected Areas). The tool will also include regional and country-level biodiversity and environmental data in priority countries. The tool is not available for viewing at present. But here is a powerpoint describing its capabilities.
CBI is providing science and technical support to assist the California Energy Commission (CEC) in planning the state’s future energy needs, which includes achieving aggressive renewable energy goals with minimal damage to natural systems. Building off of previous work completed for the Desert Renewable Energy Conservation Plan (DRECP), CBI is working to improve access and transparency of scientific data, maps and analysis. As a subset of the work, CBI is supporting the Renewable Energy Transmission Initiative 2.0 (RETI). RETI, according to the CEC, “is an open, transparent, and science-based process that will explore the abundant renewable generation resources in California and throughout the West, consider critical land use and environmental constraints, and identify potential transmission opportunities that could access and integrate renewable energy with the most environmental, economic, and community benefits.”
CBI is developing additional data, models, tools, and technical assistance that align with statewide energy and climate change adaptation planning. This work extends the information and tools previously built for the DRECP planning region to other areas of the state particularly in areas with high renewable energy potential.
Climate change and related impacts such as drought and wildfire are growing concerns throughout the state. In response, CBI is developing additional datasets and visualization applications to put this information into statewide context. CBI will deliver this data and information to the CEC and other California State agencies.
The U.S. Forest Service, Oregon State University, and Conservation Biology Institute have collaboratively developed the Seedlot Selection Tool to help forest managers match tree seed collections (called seedlots) with planting sites to help ensure the resilience of forests in a changing climate.
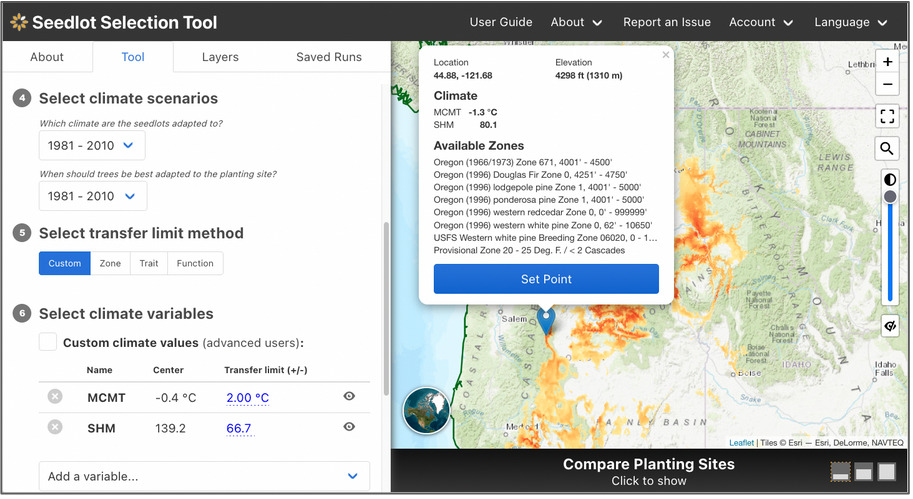
The Seedlot Selection Tool (or SST) is a free web-based decision-support tool that can be used to map planting locations based on either current climate data or a range of possible future climates across the conterminous U.S. and Mexico. Users can select a tree species, a climate scenario and relevant climate variables for the species, and other parameters to identify sources of seedlots appropriate for planting on a particular site or planting sites that are appropriate for planting seedlings from a particular seedlot. A valuable planning and educational tool, the SST helps explore possible future conditions, assess risk, and plan potential responses as part of a decision about which seedlot seedlings will be best adapted to a particular planting site in the future.

Seedlot Selection Tool Guidebook for US Forest Service Region 6 Silviculturists
Seedlot Selection Tool Video Tutorial for US Forest Service Region 6 Silviculturists

The SST was spearheaded by Glenn Howe at Oregon State University and Brad St. Clair at the USFS Pacific Northwest Research Station and developed by Nikolas Stevenson-Molnar, Brendan Ward, and Dominique Bachelet at CBI. Recently the USDA Climate Hub and USFS Region 6 staff worked with CBI to develop a step-by-step Guidebook and Video Tutorial for the Seedlot Selection Tool for Region 6 Silviculturists. These materials are useful to anyone who wants to learn about the use of this resource.
You may access the SST and detailed instructions at https://seedlotselectiontool.org/sst/.
Please see the USDA Climate Hub Seedlot Selection Tool Web Page for more information about the Guidebook and Tutorial Video.
Support for the SST came from the USFS, OSU, CBI, and the USDA Northwest Climate Hub.
CBI is expanding on previous work with the Peninsular Florida Landscape Conservation Cooperative (PFLCC) to further develop the PFLCC Simple Viewer to provide greater functionality and flexibility. In March 2017, CBI worked with PFLCC to incorporate PFLCC’s Blueprint version 1.0 into the viewer, and also created new reporting functionality to export on-screen results to PDF. In July 2017, CBI introduced the ability to aggregate multiple watersheds for display of summary information. This is particularly useful for users whose areas of interest and jurisdictions span multiple watersheds.
CBI is currently working on creating a Conservation Actions Tracker that will be added to the PFLCC Conservation Planning Atlas developed by CBI using Data Basin. This Conservation Actions Tracker will to allow users throughout Florida to enter information about conservation actions on the landscape – such as restoration activities – using an intuitive map-oriented interface. Users will also be able to explore any conservation actions in the system, and discover opportunities for collaboration and shared impact.
CBI is in the process of designing a new interactive application to showcase the PFLCC climate change adaptation guide so that users will be able to use interactive maps and data visualization to gain a greater understanding of climate change adaptations within Florida landscapes.
CBI is producing a spatial decision support system (SDSS) for the Sonoma County Agricultural Preservation and Open Space District (“District”). The District works to conserve habitat, watersheds, and agriculture for people and wildlife in Sonoma County, CA, and is pursuing the development of an SDSS to help guide its land conservation strategies. First, the SDSS will support the development of a ten-year, comprehensive county-wide conservation plan through analysis of multiple conservation themes. It will also assist parcel-scale decisions relating to individual conservation easement projects. In addition, it will produce county-wide outputs (e.g., high priority habitat areas) that can be integrated with other open space planning and scenario-building processes (e.g., the County General Plan). Finally, the SDSS framework—its hierarchical data integration architecture—and supporting data will be published online as an interactive, Web-based program so that the public can explore and learn about the District’s prioritization methods and priority conservation areas.
On the technical end, the Sonoma County SDSS will use an expansion of CBI’s Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (EEMS) along with a new habitat representation algorithm and an expansion of the Linkage Mapper connectivity model (from circuitscape.org). Please contact John Gallo with any questions or comments.
CBI is working with Utah’s Division of Wildlife Resources (DWR) and The Bureau of Land Management to develop decision support models to inform current conservation initiatives in Utah and throughout the Colorado Plateau ecoregion. Based on previous REA (Rapid Ecoregional Assessment) work, CBI is updating the existing terrestrial landscape and aquatic intactness models for the Colorado Plateau ecoregion as well as updating habitat profiles for a number of identified conservation elements of interest (largely native species and communities). CBI is extending the models to cover the entire state of Utah as well as fine-tuning the models to be more effective at answering different management questions over smaller geographic areas.
CBI is also updating a previously created climate stress logic model with the most recent climate data from the 5th Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report as well as carryout some new analyses. For example, mapping potential climate refugia – areas where plants and animals may find shelter from changes in climatic conditions. CBI is also examining past and future climate variability to model climate velocity, which is the speed along the Earth’s surface needed to maintain constant climate conditions with the rationale being that species survival may depend as much on keeping pace with moving climate as the climate’s ultimate persistence. Results of the climate modeling will illustrate at the landscape level the degree to which locations in the landscape will be impacted by climate stress over the next century and help estimate the likelihood that certain species will survive shifting suitable habitat conditions.
Click here to see the console.
The Conservation Biology Institute, in collaboration with Ted Weller (USFS – Pacific Southwest Research Station) is expanding the functionality of Data Basin to create a clearinghouse for migratory bat detection data. This new functionality will allow users to: (1) import location-aware spreadsheet data into Data Basin; (2) dynamically visualize these locations and their attributes (such as number of bats of a particular species) within the interactive map; and, (3) explore charts of time series records across one or more locations. Additional tools under development will allow aggregation into a single master dataset, support form-based imports to more easily capture site and detector information from researchers during upload, and support export of records into spatial and non-spatial outputs.
More information about the exciting implications of this project can be found within an article on The Wildlife Society website.
