A Regional Conservation Investment Strategy (RCIS) is a voluntary, non-regulatory, and non-binding conservation assessment that includes information and analyses relating to the conservation of focal species, their associated habitats, and the conservation status of the RCIS land base. The RCIS program, which is administered by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife, was created by state bill AB 2087. This conservation strategy is intended to guide conservation investments and advance mitigation in RCIS areas. CBI provided scientific and technical support to ICF International, who led the development of a pilot RCIS for the Antelope Valley in LA County. Implementation of this strategy is intended to sustain and enhance focal species and their habitats in the face of climate change and other stressors such as habitat loss and fragmentation.
Working with Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife, Oregon Department of Transportation, US Fish and Wildlife Service, and other governmental and non-governmental partners, CBI is reviewing the current state of knowledge and is developing a wildlife and habitat connectivity blueprint for the State of Oregon, including the plan for generating a number of useful map-based products and online tools that will address planning at multiple scales across the state. This initial phase is expected to conclude in January 2018 with testing of the blueprint being carried out for a subset of the state (Coast Range and Klamath ecoregions) through different funding.
CBI is playing a key role in improving the health and resilience of wetland ecosystems in Southern California in a partnership with the Southern California Wetlands Recovery Project (SCWRP). The newly-released Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool provides data access and decision-support technology for SCWRP’s new Regional Strategy 2018, a recovery plan for tidal and non-tidal wetlands from Point Conception to the Mexican border.
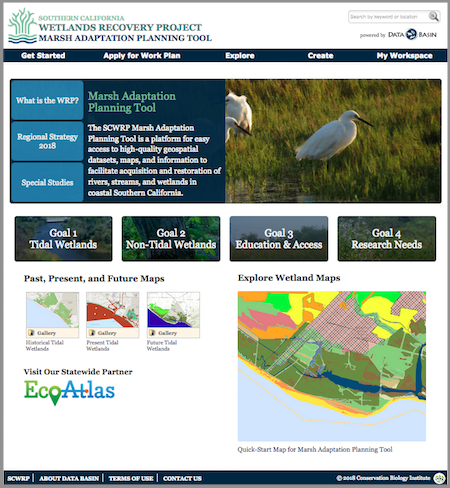
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool homepage, with access to the Regional Strategy 2018, the spatial data that informed its development, and a special tool for planning projects that will contribute to its Work Plan.
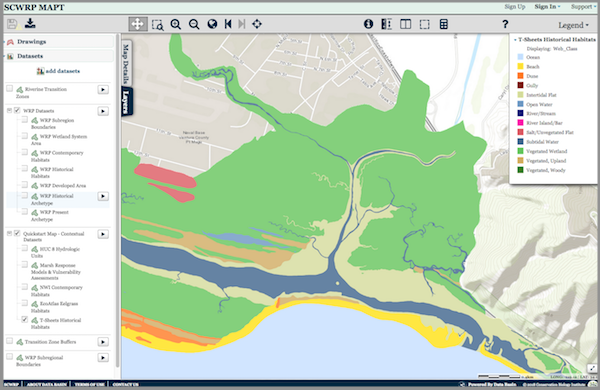
Above: The MAPT’s “Quick-Start Map” that allows the user to explore Southern California’s wetlands. Layers depicting historical and present-day wetlands, important transitions zones, and other features can be turned on and off for quick comparison. The map and its data layers can be downloaded for use in GIS, or saved and used with any other layers in Data Basin.
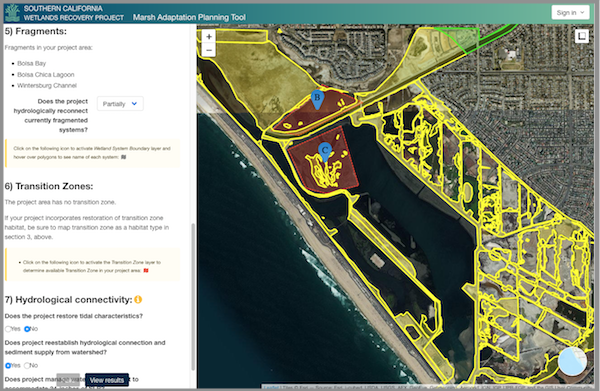
Above: The Marsh Adaptation Planning Tool’s project planning utility, where project proponents can use Regional Strategy 2018 spatial data, habitat types, and goals and objectives to inform the planning of a project and apply to have it included in the SCWRP Work Plan.
CBI is supporting the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) in its work to develop a strategic, comprehensive approach for conducting inventory, monitoring, and assessments that respond to the priorities of the whole agency instead of individual or programmatic needs. Many of today’s management decisions require a landscape approach to acquiring and analyzing information about forests and rangelands. Therefore an effective inventory, monitoring and assessment system requires working across organizational boundaries to determine common goals, avoid duplication and build on common information needs. CBI will provide support to assess existing data collection, management and storage methods for the USFS Region 8 and make recommendations regarding the relationship agency data has with current decision support processes.
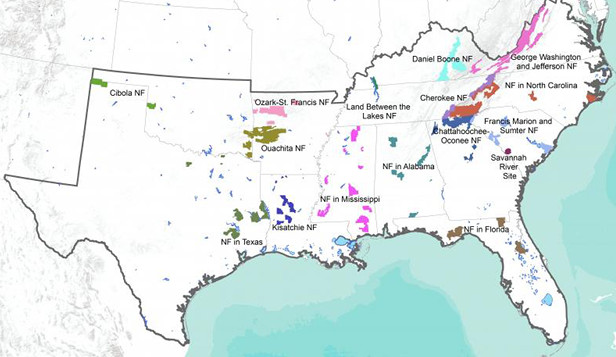
While the U.S. Forest Service National Forest Review projects are focused at the individual Forest level, the Census of Inventory, Monitoring, and Assessment Activities is focused on Region 8, which encompasses 15 Forests and covers 13 states in the southeastern United States.
CBI is expanding on previous work with the Peninsular Florida Landscape Conservation Cooperative (PFLCC) to further develop the PFLCC Simple Viewer to provide greater functionality and flexibility. In March 2017, CBI worked with PFLCC to incorporate PFLCC’s Blueprint version 1.0 into the viewer, and also created new reporting functionality to export on-screen results to PDF. In July 2017, CBI introduced the ability to aggregate multiple watersheds for display of summary information. This is particularly useful for users whose areas of interest and jurisdictions span multiple watersheds.
CBI is currently working on creating a Conservation Actions Tracker that will be added to the PFLCC Conservation Planning Atlas developed by CBI using Data Basin. This Conservation Actions Tracker will to allow users throughout Florida to enter information about conservation actions on the landscape – such as restoration activities – using an intuitive map-oriented interface. Users will also be able to explore any conservation actions in the system, and discover opportunities for collaboration and shared impact.
CBI is in the process of designing a new interactive application to showcase the PFLCC climate change adaptation guide so that users will be able to use interactive maps and data visualization to gain a greater understanding of climate change adaptations within Florida landscapes.
The Desert Renewable Energy Conservation Plan (DRECP), a major component of California’s renewable energy planning efforts, is designed to provide effective protection and conservation of desert ecosystems while allowing for the appropriate development of renewable energy projects. Approximately 22.5 million acres of federal and non-federal California desert land are in the DRECP Plan Area. The federal portion of plan area was released by the Bureau of Land Management as a Land Use Plan Amendment (LUPA). The project is now transitioning into Phase II, which focuses on county-level planning designed to work in conjunction with the LUPA.
During Phase I of the project, CBI provided science support for this ambitious planning process including a wide range of spatial models and assessments (e.g., species distribution, intactness, conservation value, and climate change). CBI also developed and continues to maintain the DRECP Gateway (launched on September 26, 2014) and various interpretation applications to support the determination of the Final Plan and its implementation. One example of an interpretation application is the DRECP Climate Console, which was designed to allow users to explore climate projections to better understand how climate change could alter ecosystems in the California desert. It provides science-based and actionable climate data to encourage smarter, more comprehensive landscape-level conservation planning efforts and decisions.
During Phase II of the project, CBI is customizing the Gateway to support the adaptive management aspects of the LUPA and to support the county-level planning processes.
To access the gateway, please visit http://drecp.databasin.org/
To access the Climate Console, please visit http://drecp.consbio.webfactional.com/climate
To learn more about the DRECP, please visit www.drecp.org or visit the Data Basin Guide and Case Study about DRECP at http://databasin.org/articles/1408e0eed6754d68a06047aaa0e64c2b
The San Joaquin Valley Data Basin Gateway was created to support a multi-stakeholder effort to identify least conflict lands for utility scale solar development in the San Joaquin Valley in Central California. Stakeholders represented include the solar industry, farming community, ranching community, and environmental community. Each stakeholder group addressed the least conflict question from their perspectives and generated map-based results. After compiling the results, around 470,000 acres of land was identified as potentially desirable to solar developers and least conflict from the standpoint of the other groups. Phase I is complete with a final report due out in February 2016, but the Gateway persists with an extremely valuable data library (~600 datasets pertinent to the region) and other content, and stakeholders have expressed interest in continuing to use the system to continue refining the work into the future.
CBI is providing science and technical support to assist the California Energy Commission (CEC) in planning the state’s future energy needs, which includes achieving aggressive renewable energy goals with minimal damage to natural systems. Building off of previous work completed for the Desert Renewable Energy Conservation Plan (DRECP), CBI is working to improve access and transparency of scientific data, maps and analysis. As a subset of the work, CBI is supporting the Renewable Energy Transmission Initiative 2.0 (RETI). RETI, according to the CEC, “is an open, transparent, and science-based process that will explore the abundant renewable generation resources in California and throughout the West, consider critical land use and environmental constraints, and identify potential transmission opportunities that could access and integrate renewable energy with the most environmental, economic, and community benefits.”
CBI is developing additional data, models, tools, and technical assistance that align with statewide energy and climate change adaptation planning. This work extends the information and tools previously built for the DRECP planning region to other areas of the state particularly in areas with high renewable energy potential.
Climate change and related impacts such as drought and wildfire are growing concerns throughout the state. In response, CBI is developing additional datasets and visualization applications to put this information into statewide context. CBI will deliver this data and information to the CEC and other California State agencies.
The Santa Barbara County Conservation Blueprint provides a common language and platform for publicly available data to support in depth conversations and informed decisions about the Santa Barbara County landscape. This collaborative project aims to describe the current landscape, natural resources, and community values about land in Santa Barbara County.
CBI is supporting this process for the Santa Barbara County region. The process is led by the Land Trust for Santa Barbara County, Cachuma Resource Conservation District, and the Santa Barbara Foundation’s LEAF Initiative to develop a Conservation Gateway for Santa Barbara County. This process is also guided by a 12-member Steering Committee representing agriculture, conservation, resource management, and the natural sciences.
This data gathering and community engagement process led to a Conservation “Blueprint” (including a Data Basin Gateway) that is providing a science based decision-making platform for future conservation in the county, including acquisition, restoration and guidance for other potential land management opportunities. In the long-term, this process is expected to include collective visioning, tool- sharing and collaborative strategies. The effort will strengthen the region’s integrity by building community, sharing information, and facilitating stewardship.
Visit www.sbcblueprint.net to learn more about the Blueprint project and explore the online Atlas.
