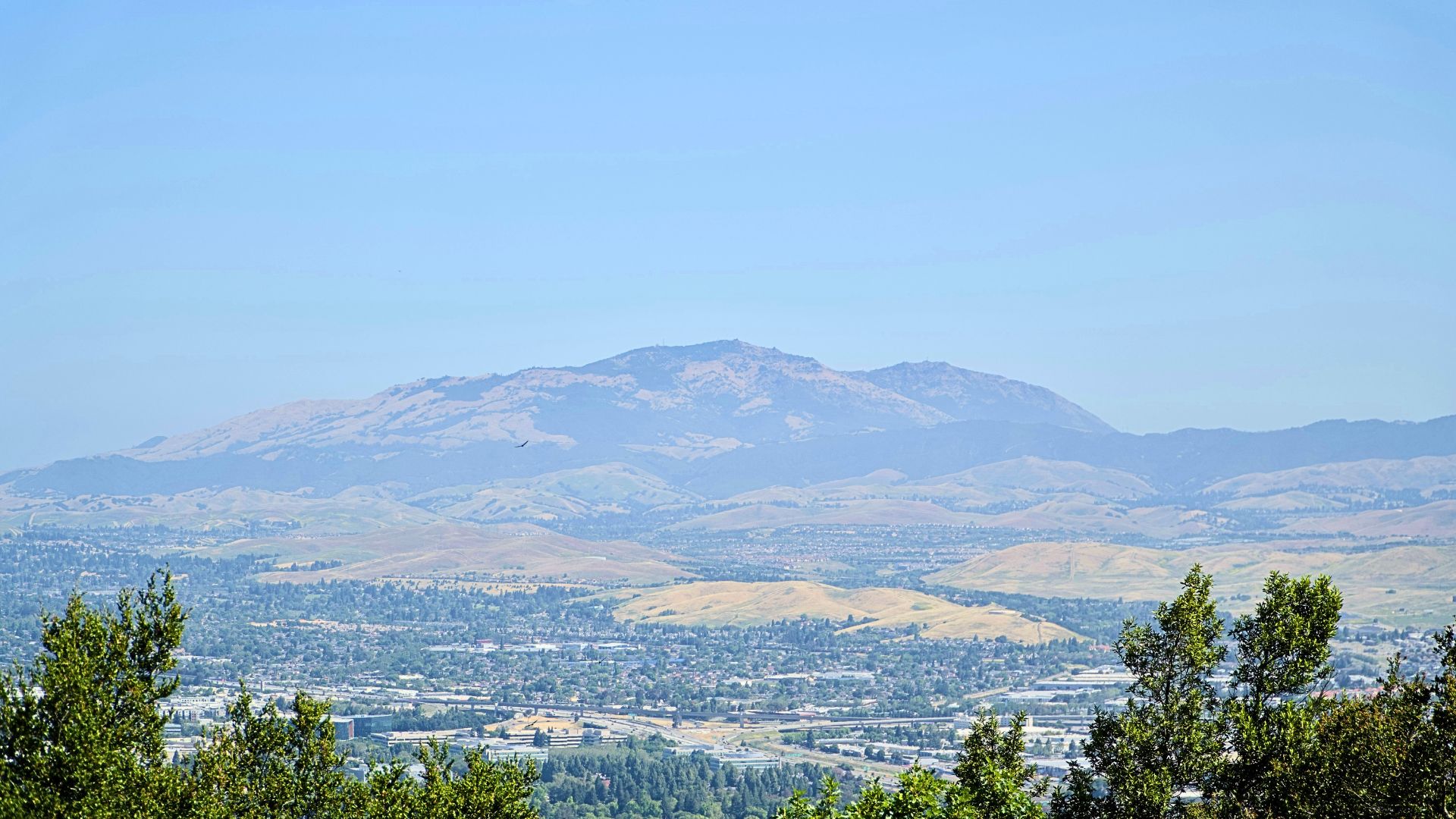
Felidae Conservation Fund, Bay Area Puma Project, and Conservation Biology Institute co-produce an analysis and project to improve the connection to and from Mount Diablo
Description
The project aims to address the pressing issue of habitat fragmentation and lack of connectivity for mountain lions in the East Bay Diablo Range of the San Francisco Bay Area in California. The current situation poses a significant risk of inbreeding and local extinctions among these iconic predators, further threatening the fragile biodiversity of the region.To tackle this challenge, our project will identify potential linkages and barriers to movement for mountain lions, with the goal of establishing evidence-based conservation strategies. We will employ cutting-edge connectivity modeling and mapping techniques. We will also utilize state-of-the-art remote-sensing camera arrays to capture and analyze wildlife movement patterns in the East Bay Diablo Range. These camera arrays will provide valuable data to ground-truth linkage models, allowing us to accurately identify potential corridors and barriers for mountain lion movement. By combining cutting-edge modeling techniques and technology with on-the-ground fieldwork, we will enhance the precision and effectiveness of our conservation strategies, ensuring that our efforts are grounded in robust scientific evidence.
By identifying and restoring crucial corridors, we aim to mitigate the adverse effects of habitat isolation, promote gene flow, and safeguard genetic diversity among mountain lion populations. This, in turn, will contribute to the overall health and resilience of the East Bay Diablo Range ecosystem.
The project’s success will rely on a multidisciplinary approach, combining scientific research, community involvement, and policy advocacy. By addressing the challenges of habitat fragmentation and promoting connectivity, we aim to ensure the long-term persistence of mountain lions in the East Bay Diablo Range while preserving the rich biodiversity that characterizes this unique region.
Overall, this project represents a vital opportunity to protect and restore critical habitats, prevent local extinctions, and secure the future of mountain lions in the San Francisco Bay Area. By investing in the conservation of these iconic predators, we will safeguard the ecological integrity of the East Bay Diablo Range and also enhance the overall health and resilience of the region for generations to come.
The Project Page for this is periodically updated, and is currently located at
https://felidaefund.org/projects/research/pumalink

Because of the importance of the Central Valley of California to shorebirds along the Pacific Flyway, considerable conservation investments have been made in the area’s agricultural fields and managed wetlands. Through their BirdReturns and Bid4Birds programs, The Nature Conservancy and the California Ricelands Waterbird Foundation pay rice farmers to flood fields to decompose post-harvest rice thatch and, in doing so, create habitat for shorebirds. Previous research by CBI and The Nature Conservancy researchers found that shorebird density (birds/hectare) increased with earlier fall flooding and in fields managed to be approximately 50% flooded, 5-10 cm deep, and with minimal straw or stubble cover in fall. Lower soil clay content and flooding consistency – either at a site that is continually flooded over many months or a site that has been flooded in previous years – was also associated with higher shorebird density. Finally, the team found preliminary evidence that fields flooded by groundwater, instead of surface water, were associated with higher shorebird density. These findings are important for guiding continued shorebird management in agricultural landscapes.
Combining the five years of data on shorebird abundance used in the original study with an additional five years of more recent data, we are going to expand our preliminary analysis on the importance of water source on shorebird abundance. Specifically, we are going to explore whether more shorebirds are found in fields flooded with surface water versus groundwater. Assuming that shorebirds prefer groundwater in the expanded analysis, our next priority is to explore why, where our first hypothesis is water quality. Using a number of public resources that sample groundwater quality (nitrates, sodium, and arsenic) and surface water quality (pH, turbidity, temperature, conductance, and dissolved oxygen), we will explore whether shorebird abundance is associated with any of these water metrics. Determining the best practices for habitat creation in agricultural landscapes is critically important for conservation and recovery of declining shorebird populations.
Providing Tools for USDA Monitoring and Assessment
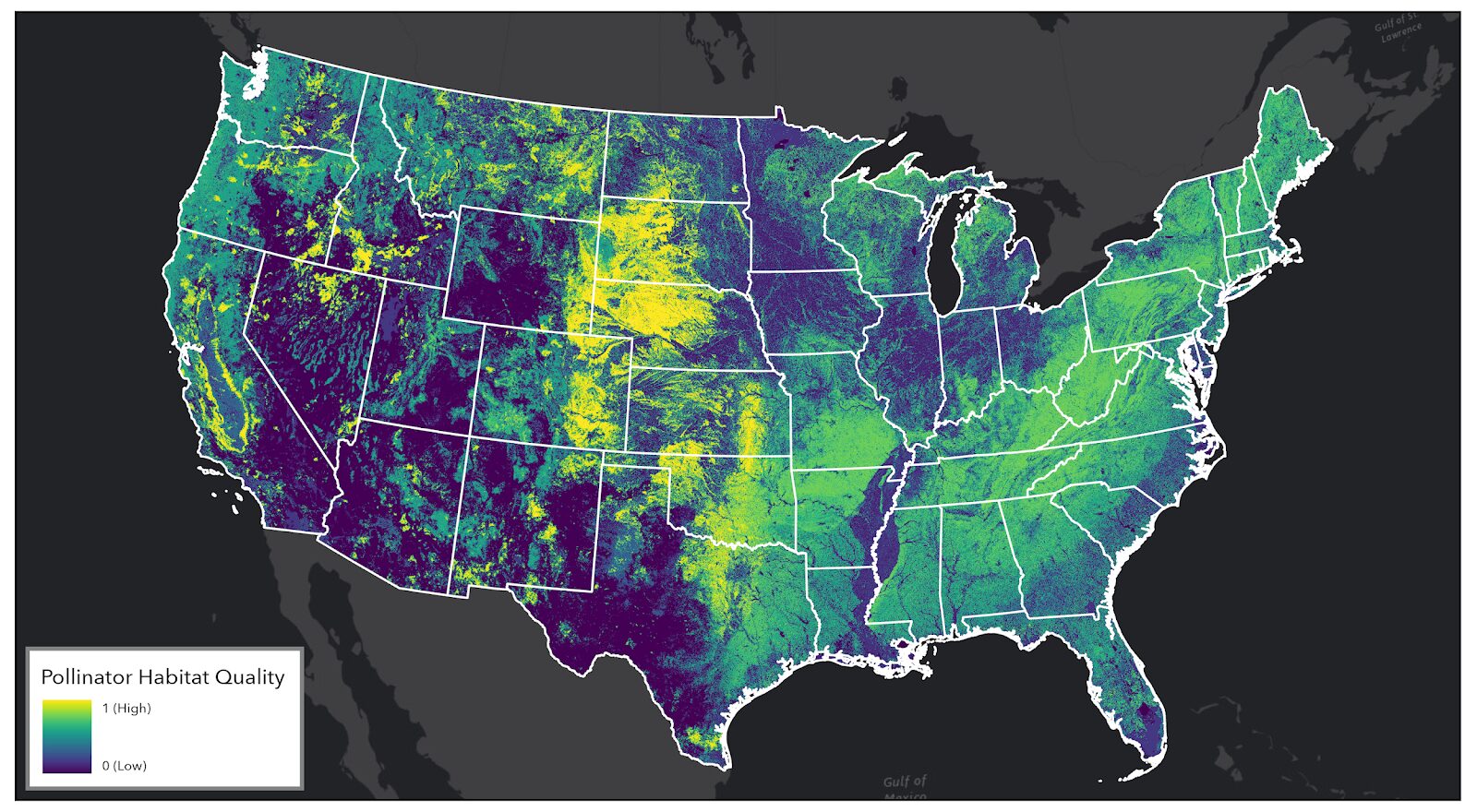
CBI is using the latest remote sensing, machine learning, and modeling approaches to assess the quality of grasslands and pollinator habitat. Outputs from this analysis will be delivered to USDA through an online-decision support system, designed and built by CBI, called the USDA Conservation Toolkit. This suite of map-based tools will support the USDA Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) and other land-based conservation and restoration programs operating across the United States. CRP currently covers ~24.8 million acres of working lands nationwide.
Goal: Assess ecosystems services across the CRP portfolio
- Generate products to support USDA policies and program initiatives
- Provide actionable conservation intelligence

Targets
- Quantify foundational supporting ecosystem services across CRP enrollments
- Grasslands ecosystem quality
- Pollinator habitat quality
- Incorporate resulting spatial data and metrics into online applications, allowing for program reporting at multiple scales
- A priority for this effort is to quantify the CRP national portfolio return on investment, screening enrolled farms, and assessing at state, regional and national scales
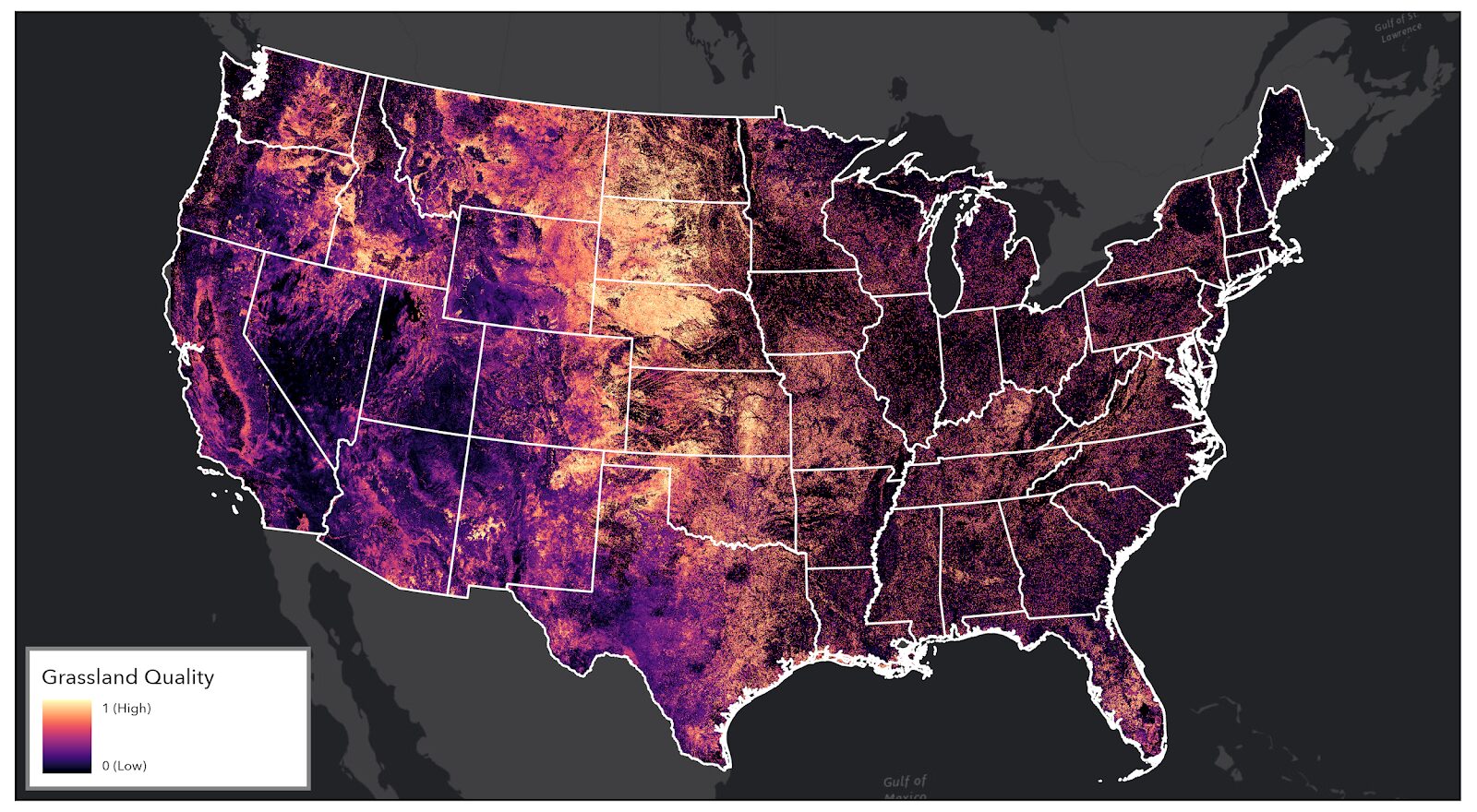
CBI CRP Grassland Quality Model – Overview
Components
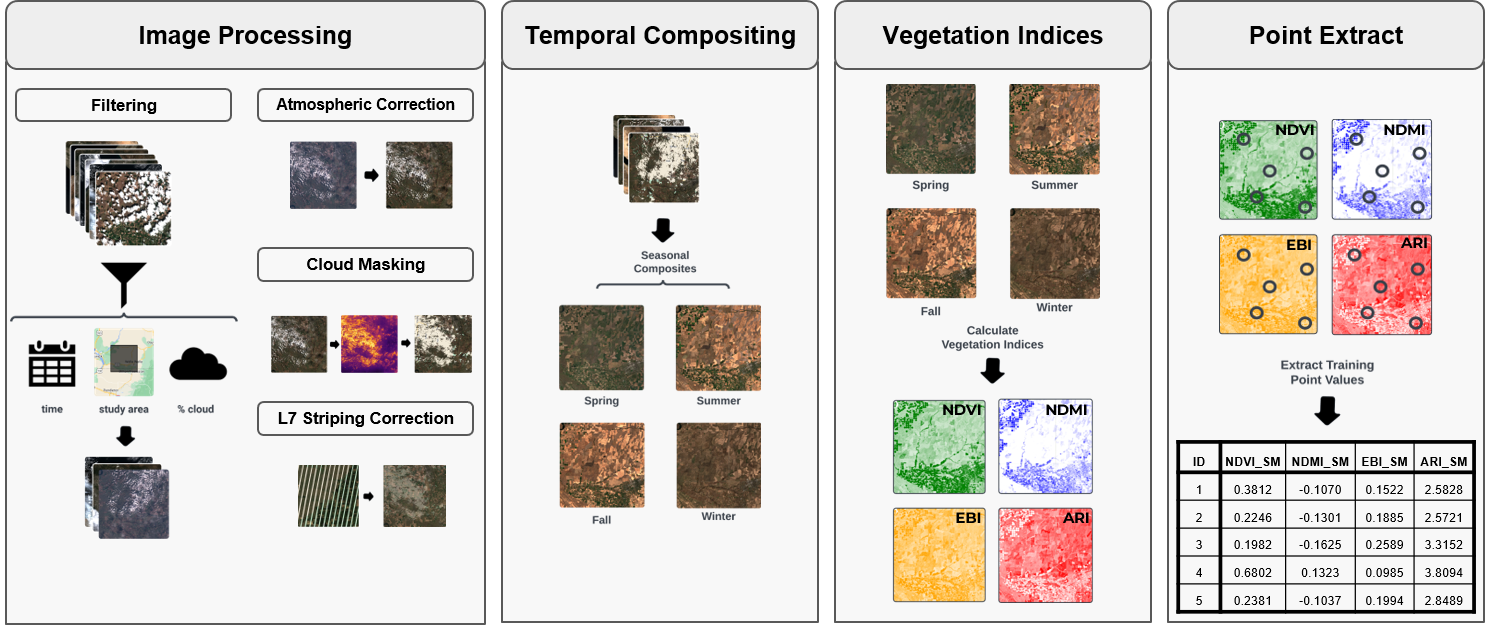
- Integrative, comprehensive approach to modeling using the best available spatial data and remotely sensed metrics (e.g. National vegetation surveys, NLCD, Rangeland Analysis Platform (RAP), custom CBI products)
- Leverages outputs from the Google Earth Engine (GEE) cloud-computing platform with CBI’s customized library of 200+ vegetation indices
What does it tell us?
- Indicator for ecosystem health, form, function, and supporting services strength, based on the USDA grassland operational definition (USDA-NRCS 2024, National Resources Inventory Grazing Land On-Site Data Collection Handbook)
- Complements existing frameworks (Rangeland Health Assessment) and other modeling efforts (RAP, K. Barnes 2024)
What does it offer USDA?
- Multi-scale (non-monetary), valuation of ecosystem condition for CRP enrolled lands and surrounding landscape
- Insights on baseline field-level condition and landscape-level spatial analytics for CRP assessment and reporting
- Illustrates CRP return on investment at a programmatic scale and quantifies enrolled land performance with nuanced metrics
How is it unique?
- Hierarchical measure of grassland ecosystem vigor, community composition, and resilience
- Expandable framework produces multidimensional metrics to quantify patterns across the landscape
- Summarizes information across CRP farms and practices
- Offers insights on baseline current state and local condition at multiple scales
Pollinator Habitat Quality Model – Overview
Components
- Integrative, comprehensive approach to modeling using the best available spatial data and remotely sensed metrics (e.g. US National Phenology Network, NLCD, Rangeland Analysis Platform (RAP), NatureServe Explorer, custom CBI products)
What does it tell us?
- Describes pollinator natural resource needs and spatial use of the landscape
- Indicator for pollinator population health and pollination service strength
- Spatial complement to on-ground pollinator assessments funded by USDA

What does it offer USDA?
- Multi-dimensional, non-monetary valuation of pollinator habitat
- Foundation for field to landscape-level spatial analytics for CRP assessment and reporting
- Illustrates CRP return on investment at a programmatic scale and quantifies enrolled land performance with nuanced metrics
How is it unique?
- Builds on the benchmark InVest© model framework
- Informed by 300,000 bee observations from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF)
- Innovations for bee flight, nesting, and floral suitability estimates
Abstract:
“Wildfires can be devastating for social and ecological systems, but the recovery period after wildfire presents opportunities to reduce future risk through adaptation. We use a collective case study approach to systematically compare social and ecological recovery following four major fire events in Australia and the United States: the 1998 wildfires in northeastern Florida; the 2003 Cedar fire in southern California; the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires in Victoria, southeastern Australia; and the 2011 Bastrop fires in Texas. Fires spurred similar policy changes, with an emphasis on education, land use planning, suppression/emergency response, and vegetation management. However, there was little information available in peer-reviewed literature about social recovery, ecological recovery was mostly studied short term, and feedbacks between social and ecological outcomes went largely uncon- sidered. Strategic and holistic approaches to wildfire recovery that consider linkages within and between social–ecological systems will be increasingly critical to determine if recovery leads to adaptation or recreates vulnerability.
Abstract:
Ecological connectivity is increasingly acknowledged as crucial for biodiversity conservation. Iverson et al. suggest that increasing stewardship to ensure permeability is a better approach than protecting linkages between protected areas. We argue that the optimal approach depends on the landscape context, conservation goals, and species involved and suggest that linkage plans can prioritize specific places for protection and improved management. However, when using connectivity models as predictive tools, model validation is vital. We commend Iverson et al. for assessing whether modeled linkages were important predictors of species presence. We disagree, though, with the authors’ conclusion that their findings challenge the theory and practice of modeling linkages and explain that the reason may be the misalignment of the validation assumptions with model objectives. We offer our perspective on best practices for conducting validation studies and note factors to consider with respect to data used for model validation and model expectations.
Map-based tools that support the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) of USDA and other land-based conservation and restoration programs in the U.S
USDA contracted the Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) to design and build a free online easy-to-use Plant and Vendor finder to support the producers associated with the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP). However, the tool is not limited to the CRP program and can serve the needs of any land stewardship effort requiring native seeds/seedlings. In partnership with the Institute for Applied Ecology (IAE) we have added features to address the needs of the Native Seed Network and significantly expanded the native seed customer and vendor base.
The seed and vendor finder can be found here: Plant and Vendor Finder
Currently, CBI has seeded the tool with 214 vendors found through an online search from across the country with limited profiles, and 45 have voluntarily completed full profiles which includes their plant catalogue. The tool is designed for easy uploading of their profile and inventory. It also provides an opportunity for vendors without a website to have an online presence and be found by customers looking for seeds.

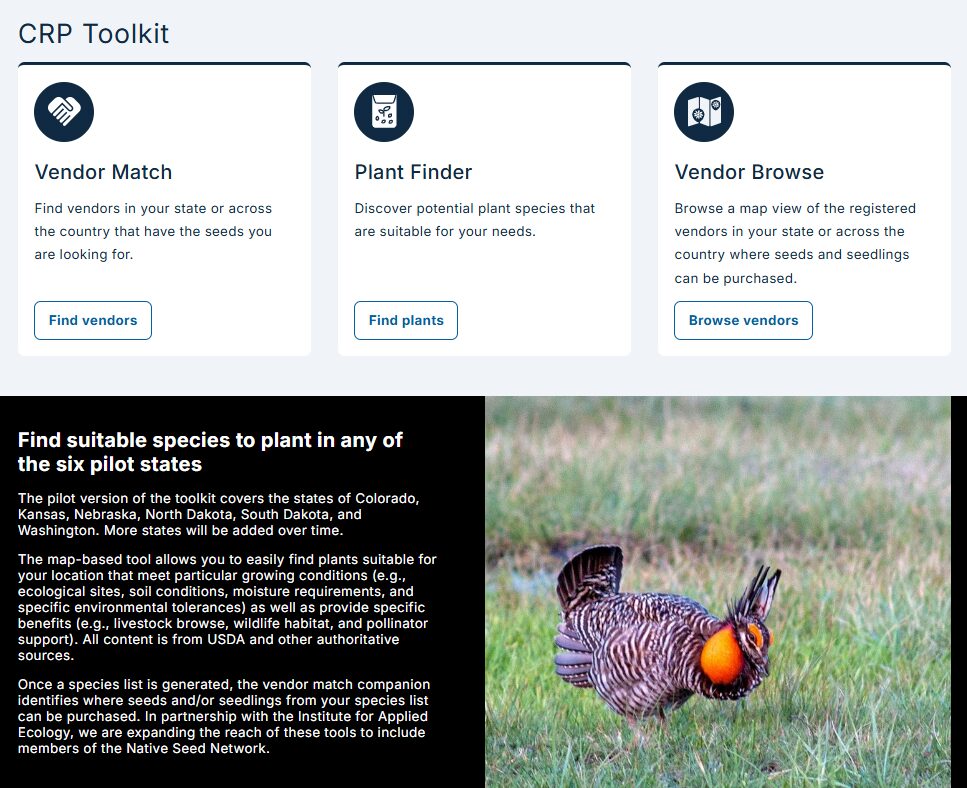
The map-based Plant Finder tool allows you to easily find plants suitable for your location that meet particular growing conditions (e.g., ecological sites, soil conditions, moisture requirements, and specific environmental tolerances) as well as provide specific benefits (e.g., livestock browse, wildlife habitat, and pollinator support). Once a species list is generated, the Vendor Match tool identifies where seeds and/or seedlings from your species list can be purchased. The Vendor Browse tool allows you to easily browse a map view of the registered vendors in your state or across the country where seeds and seedlings can be purchased.
All data content is from authoritative sources, including NRCS state resources, NRCS Ecological Site program, and the USDA PLANTS database.
The vendor match and browse tools have been updated in partnership with the Institute for Applied Ecology (IAE)for the Native Seed Network. Note that IAE uses its legacy name `Seed Finder tool’ for what is essentially the same as the USDA Plant and Vendor finder tool.
Tutorial Videos
Southern California’s montane conifer forests are primarily restricted to the “sky islands” of the San Jacinto, San Bernardino, and San Gabriel Mountains. These unique ecosystems protect the upper watersheds of all of the region’s major rivers and provide ecosystem services critical to both human and ecosystem climate resilience. Managers are in a race to restore resilience to these forests, which are threatened with conversion to hardwood and shrub due to severe wildfires and regeneration failure.
This partnership between the US Forest Service, San Diego State University, and Conservation Biology Institute is applying the latest research on interactions between multiple disturbances specific to this ecoregion to plan effective conservation action.
The effort expands on research from the Connecting Wildlands and Communities project that developed a landscape-scale framework to map refugia from multiple stressors, and ongoing research projects at CBI developing dynamic wildfire and vegetation succession models for understanding the synergistic impacts of climate change, land use change, and different management scenarios.
The team will work with scientists and managers to build interactive spatial models using CBI’s Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (EEMS) with location-specific data to support the collaborative development of a conservation strategy customized to address the threats faced by southern California’s montane forests.
By disrupting wildfire regimes, climate and land use change transform ecosystems, alter carbon budgets, and drive socio-economic impacts in California. We propose to quantify how projected peri-urban growth in the wildland urban interface, climate change, and local management actions influence wildfire activity and downstream effects on vegetation transitions, carbon release, biodiversity, and vulnerable human communities.
We will model wildfire risk as a function of a limited set of stakeholder-guided, realistic future scenarios, using the LANDIS-II simulation model. Past studies have shown the importance of human ignition location and timing on wildfire activity in Southern California, a mechanism we will explore using different land use change scenarios.
We will also model and analyze the potential influence of increasing atmospheric aridity on fire size and severity in forests and compare these effects to adjacent shrubland plant communities.
Taken together, climate, land use, and other environmental variables can lead to fire-driven vegetation type conversion, which can influence carbon sequestration, biodiversity, and even future fire risk to human communities.
Finally, we will explicitly evaluate how different modeled management actions influence wildfire, plant succession, and carbon sequestration. The resulting maps and spatial products will help managers prioritize locations for conservation and management actions. Overlaying maps of vulnerable human communities and biodiversity hotspots with future wildfire change and downstream impacts can better define locations for priority action to facilitate co-benefits to human and natural resources. This research will contribute to scientific publications and be directly relevant to managers, including the Southern California Montane Forests Project.
The San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance (SDZWA) is a world-renowned conservation organization with a 1800-acre zoo, the Safari Park, that houses more than 2600 animal and 3500 plant species. Located in Escondido (northern San Diego County), the Safari Park also includes a 800-acre biodiversity preserve with some of the most well-preserved, California-endemic coastal sage habitat.
In 2007, the Witch fire burned through 600 acres of the biodiversity reserve and stopped just outside the Safari Park borders. Since then, the SDZWA has transformed their in-house wildfire preparedness program, including hiring a team of dedicated wildfire suppression staff, fire suppression equipment boxes scattered throughout the park, an infrared and visible spectrum camera array for early ignition detection, and a 8500-gallon water tank for aerial suppression by local first responders.
While these investments in wildfire readiness are important for protecting the Safari Park grounds, landscape-scale risk analyses are needed to determine where fires may start and spread outside of park boundaries and which additional management activities could mitigate risk from fires originating beyond Park borders. Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) and Dudek have proposed to co-create the needed wildfire risk analysis for the SDZWA Safari Park.
At the core of the risk analysis is a fusion and comparison between two commonly employed modeling efforts used in
CBI is a partner in producing a statewide wildlife connectivity ensemble model and associated mapped data in support of a connectivity action plan for the state, which is under development. The modeling will identify priority areas across the state in need of some form of mitigation to promote wildlife connectivity and reduce wildlife/vehicle collisions at the same time. The co-production process includes the close collaboration with an active Technical Advisory Group. The project is being funded by the Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife.
