The Columbia Plateau in eastern Washington supports productive farmland and rangeland as well as native shrub-steppe habitat of which only 40% remains intact. The region also contains some of the most sought after land in the state for utility scale solar energy development, which is an important component of its future energy portfolio that strives to produce 80% of the state’s electricity from renewable sources by 2030 and 100% carbon-free by 2040.
CBI has been chosen by the Washington State University Energy Program to provide the science and mapping component in support of a voluntary, collaborative effort that brings stakeholders together in order to identify areas of least-conflict between solar energy development and other important ecological, economic, and social values in order to meet the state’s carbon-free energy goals. CBI’s contribution to this process is based on the successful pilot to this approach in the San Joaquin Valley in California. The project will include a new Data Basin gateway, which is a customized site for accessing the science and mapping resources for this project.
See the recent brochure published by Washington State University for more information.
CBI’s easy-to-use spatial analysis and sharing platform empowering people to create maps and collaborate from anywhere in the world. Has a growing list of 44,000+ users, 33,000+ datasets to choose from, and over 1000+ active collaborative groups working on a diverse set of problems.
“Data Basin has provided a fantastic means of sharing information with collaborators and intended users of data products from multiple projects. The intuitive design of the platform has meant that the learning curve for non-GIS users to meaningfully interact with my spatial data has been negligible, even as the more technical underpinnings (e.g., ability to connect with data hosted on ScienceBase) have saved me time and effort in meeting grant requirements for data sharing and documentation. Not to mention CBI staff have been phenomenally responsive to questions and suggestions along the way!” – Meredith Mclure, Lead Scientist | Conservation Science Partners
CBI will develop and apply a forest management decision-support system (DSS) for forest resilience planning in the southern Sierra Nevada that integrates the latest science on how vegetation, terrain, climate, and weather interact to influence fire risks and forest resilience. The interdisciplinary team led by CBI includes ecological modelers, forest ecologists, fire scientists, physicists, and statisticians. The core of the DSS will be a Forest Resilience Model built using EEMS (Ecosystem Evaluation Modeling System; Sheehan and Gough 2016). The DSS will be tested, refined, and applied to resilience planning in that portion of the modeling region of greatest concern to the interagency Sequoia Regional Partnership, which is working to restore ecologically resilient conditions in and near Sequoia National Forest and Sequoia-Kings Canyon National Park.
The resilience model evaluates forest resilience to fire, drought, and other factors based on landscape conditions. The DSS will allow managers to simulate fuel-reduction treatments, evaluate their effects on a range of risks and resources (e.g., fire, sequoias, fisher habitat), project the impacts into the future, and assess levels of uncertainty. The DSS and component models will help managers understand how, in concert with terrain and weather, vegetation structure influences fire behavior and forest resilience. Importantly, the DSS will for the first time consider how fire-atmosphere coupling affects fire in models to support forest planning. This will apply how vegetation structure influences fire via both fuel arrangements and air flows, and thus more accurately reflect the full picture of how vegetation treatments may affect fire and fire effects on the landscape.
The DSS will be further refined and applied to resilience planning by the Sequoia Regional Partnership, whose primary focus is reducing fire risks to giant sequoia groves, fishers, and human communities.
External Team members include: Joe Werne (NorthWest Research Associates NWRA), Christopher Wikle (Department of Statistics, University of Missouri) and David Marvin (SALO Science).
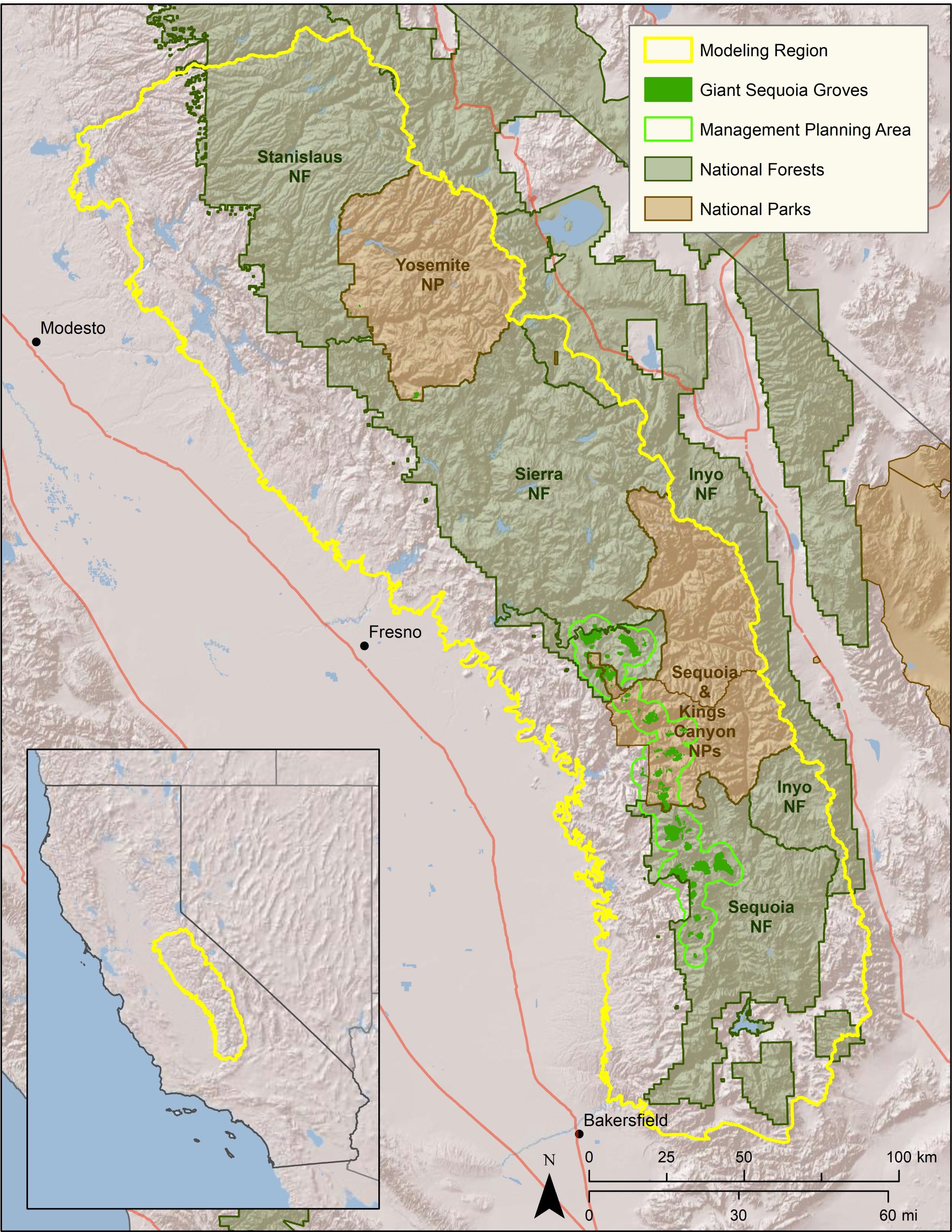 Map of project study area.
Map of project study area.
CBI has designed and launched a new Data Basin Gateway (Atlas) for the Wildlife Conservation Society Canada focusing on the Yukon Territory to assist WCS Canada researchers and their conservation partners in the region to develop effective protection of wildlife and plants being impacted by a host of environmental stressors, with special emphasis on climate change. In addition to the branded and curated gateway with relevant datasets, we have co-produced a customized application for stakeholders to view and download species distribution models (SDM) for 66 endemic plants designed to predict future changes in their distribution due to climate change. The Atlas houses relevant datasets for conservation planning in the climate-sensitive Yukon region and the tool houses the SDMs, which in combination provide powerful resources for WCS Canada and its partners to effectively plan for resilience.
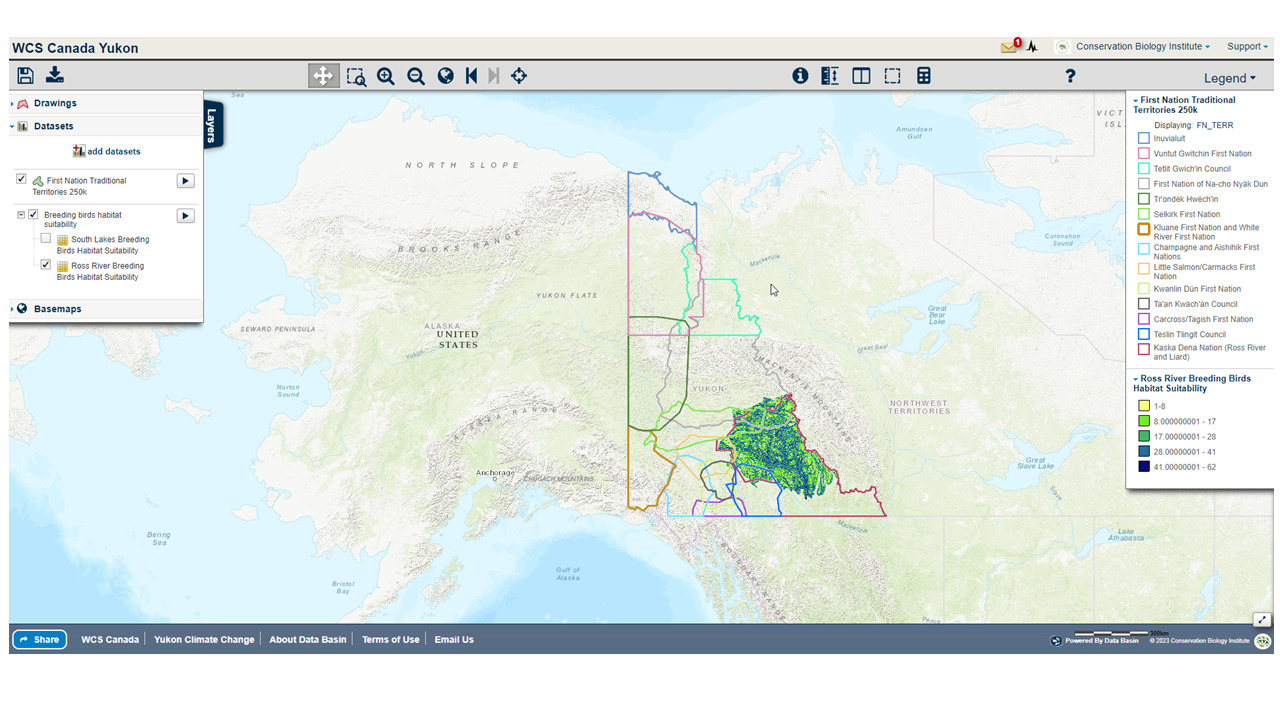
An example of a map created in the WCS Yukon Data Basin Atlas showing First Nation Territories overlaid on Ross river breeding bird habitat suitability layer
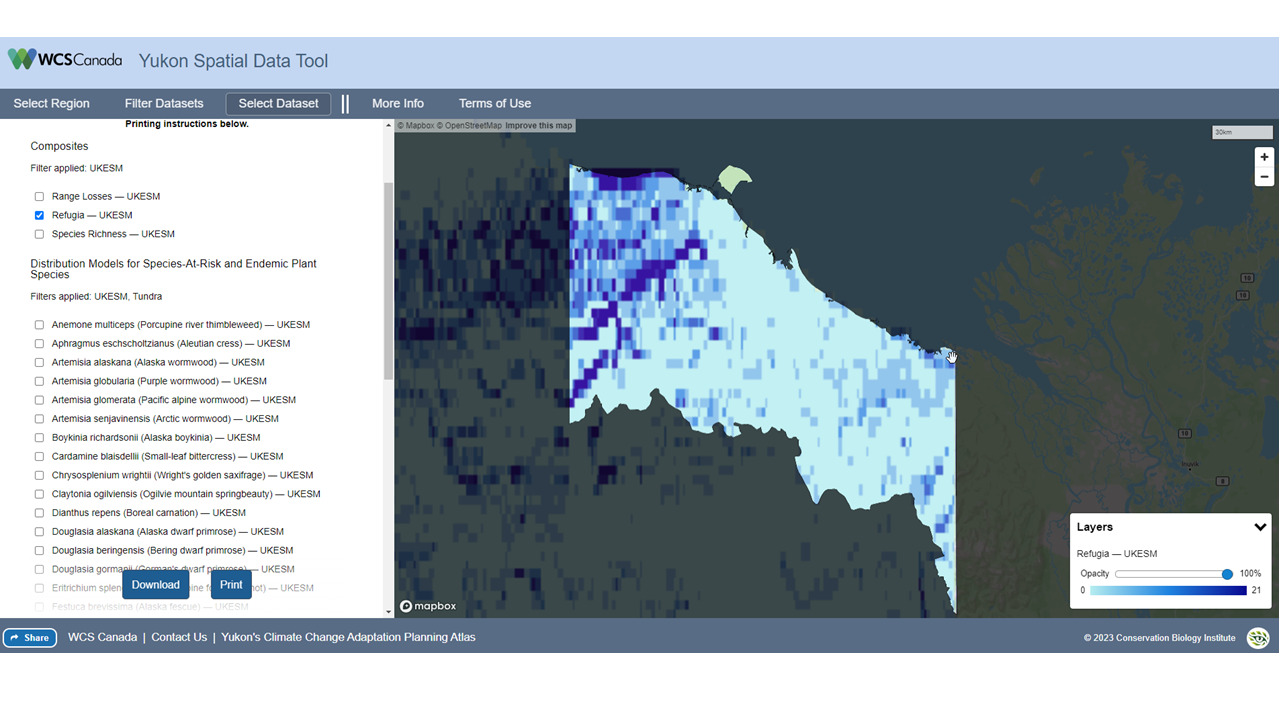
The Yukon Spatial data tool showing projected climate refugia for a Inuvialuit Planning region in the Yukon
CBI worked closely with the Department of Land Conservation Development (DLCD) and other project collaborators to carry out an expansive spatial data review and stakeholder engagement process to better understand renewable energy opportunities and constraints in Oregon. It was part of a larger effort called the Oregon Renewable Energy Siting Assessment (ORESA) project, which was funded by the U.S. Department of Defense Office of Economic Adjustment. This larger project included Oregon Department of Energy (ODOE) working closely with Oregon Department of Land Conservation and Development (DLCD) and Oregon State University’s Institute for Natural Resources (INR).
Data Basin was used to support the spatial data review process resulting in a transparent and accurate spatial data library needed for effective renewable energy planning in the state. Approximately 650 datasets were reviewed with most of them still available on Data Basin. The final Opportunities and Constraints final report was included as part of supporting materials to the larger project.
CBI is supporting the U.S. Forest Service (Region 8) in its efforts toward shared forest stewardship activities. Region 8 contains approximately 244 million acres of forestland, most of which (87%) is privately owned. The Forest Service manages around 5% of the southern forests within 14 National Forests and two Special Units with other public forests make up the remaining 8%. Because of the mixed ownership, close collaboration and shared stewardship is of paramount importance.
CBI has created a customized and curated Data Basin Gateway for the U.S. Forest Service (usfssouth.databasin.org) that supports forest stewardship organizations to access data and information to advance collaborative forest management planning. To demonstrate how to use this framework, a pilot state (North Carolina) was chosen (nc.usfssouth.databasin.org). This gateway uses the “All Lands Strategy” concept to showcase example workflows to facilitate more effective forest management and monitoring across North Carolina. CBI and the North Carolina Shared Stewardship team created supporting training materials is the form of video tutorials and how to materials.
CBI worked closely with the Natural Resource Defense Council (NRDC) to integrate relevant spatial datasets to map areas of high value from the standpoint of carbon storage and sequestration, terrestrial ecological value, and aquatic value in support of several NRDC programs, including their 30X30 campaign to protect 30% of nature in the nation by 2030. Click here to learn more about the 30×30 initiative.
Using CBI’s online modeling software called Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (or EEMS), team members were able to construct, review, and modify the models in a rigorous and highly transparent fashion from their individual remote locations. The resulting “living” models can then be used alone or together and in combination with other spatial data (e.g., existing protected areas) to add further context and insight using Data Basin. Data Basin and EEMS were effectively used to help guide NRDC’s important conservation mission.
The need to plan strategic, effective forest management is urgent in the southern Sierra Nevada, where forests have been ravaged by drought, fire, and catastrophic tree mortality. Multiple, sometimes conflicting, management objectives must be balanced, and multiple agencies need help coordinating their forest restoration actions. A common, readily accessible system evaluating landscape-scale forest condition is needed.
Conservation Biology Institute is working with the Sierra Nevada Conservancy, Sequoia National Forest, Sequoia National Parks, Sequoia Parks Conservancy, Save the Redwoods League, and others to develop forest resilience models and create a toolkit for exploring these data to support the planning of a range of resource management goals. These goals include the protection of sequoia groves, overall forest health, wildfire protection, and endangered species habitat management. The project is supported by CBI’s data sharing and mapping platform Data Basin. The project is funded by the Save the Redwood League and Sequoia National Park through its partner the Sequoia Parks Conservancy, and CAL FIRE Forest Health Research Grant Program.
Conservation Biology Institute is a partner in a new $1 million grant from a new interdisciplinary NSF program to foster building an “open knowledge network.” The inspiration for this type of network comes from Tim Berners-Lee’s (best known founder of the World-wide Web) vision for the “semantic web,” which applies tags with relationships to information on the Internet, allowing computers to do basic reasoning for improving search results and answering questions. Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google’s Assistant all use these technologies.
Dr. John Gallo co-wrote the proposal and leads CBI’s participation in the team of 13 researchers and practitioners from 10 other institutions. The team is focused on improving access and contributions to tools for analyzing geographic data called spatial decision support systems. “The proliferation of online mapping technologies has greatly increased access to and utility of these kinds of tools, and a logical next step is increasing our ability to find the appropriate data and tools for your problem and link these together for more complex analyses,” says Principal Investigator Sean Gordon of Portland State University. Through engaging stakeholders in three applied case studies (the management of wildland fire, water quality, and biodiversity conservation), the interdisciplinary project team will develop and test participatory and automated methods for finding and sharing decision-relevant information using semantic web technologies.
The new NSF Convergence Accelerator program is named for its focus on bringing together interdisciplinary teams to address one of NSF’s 10 big ideas, specifically “Harnessing the Data Revolution“, also known as building an Open Knowledge Network. Eighteen other of these phase 1 grants were made, covering areas from molecular manufacturing to tracking potentially disruptive solar phenomena. The “accelerator” part comes from the short time frame. “The application required a 3-week turn around, which is very quick for a NSF grant,” Gordon said. “Our success was largely due to having formed the Spatial Decision Support Consortium, a professional networking group four years ago, so we had ideas and people ready to go.” Each phase 1 project is eligible to submit a phase 2 proposal for up to $5 million by next March, and the process will include giving a short “pitch” talk to a panel of experts and potential funders, much like a venture capital approach.
*Learn more about this ongoing project here.
Wind energy developed in federal ocean waters off California’s coastline is poised to play an important role in diversifying the portfolio of resources that will help California achieve its 100% renewable and zero-carbon energy goals. Since 2016, the state has coordinated with other governmental partners, including the BOEM-California Renewable Energy Intergovernmental Task Force, to identify areas in federal waters off the state’s coast suitable for potential offshore wind energy development. To support this effort, the Conservation Biology Institute (CBI) is using data from the California Offshore Wind Energy Gateway to produce a robust set of spatial models, designed to synthesize information to help stakeholders and decision-makers assess the suitability of offshore wind energy development in federal waters off the coast of California. These models, created using the Environmental Evaluation Modeling System (EEMS), provide a transparent and data-driven means for assessing a range of considerations at a given location, such as existing energy potential, deployment feasibility, ocean uses, fisheries, and marine life occurrence. Together, these models can be used to inform planning processes for offshore wind energy development to maximize renewable power generation and to avoid or minimize impacts to existing ocean uses and the environment.
The California Offshore Wind Energy Modeling Platform, powered by EEMS Online technology, provides an interface where stakeholders and decision-makers can interact with and explore the models and their data sources to help support decision-making processes.
The project’s technical report, executive summary, and presentation slides are available under “Project Files”, on the right side of this page. A California Energy Commission webinar recording with a project overview can be found here.
