CBI is collaborating with the Rogue River-Siskiyou National Forest and the Klamath National Forest in their effort to conserve the Alaska yellow Cedar in its southern range where it faces extreme extinction risk due to climate change.
CBI is collaborating with the Rogue River-Siskiyou National Forest and the Klamath National Forest in their effort to conserve the Alaska yellow Cedar in its southern range, located in Southern Oregon and Northern California, where it faces extreme extinction risk due to climate change. Concerted conservation efforts are needed to develop and implement conservation and reforestation strategies, in order to manage forest tree species for sustainability in the future. CBI will help coordinate the collection of seeds from trees from 8 sites, tag and geo-reference each tree, gather information on the general health of these stands, and submit the seeds to the national seedbank in Fort Collins. In addition, current-year needles will be also collected from each seed tree for later genetic/genomics analysis by Richard Cronn and team at the Pacific Northwest Research Station of the USFS.
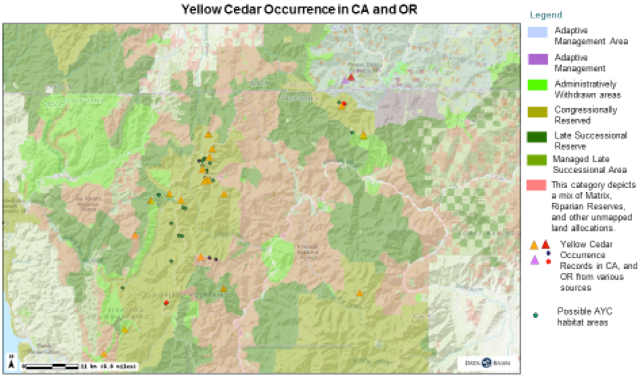
Alaska Yellow Cedar (Callitropsis nootkatensis) has an extensive range from Alaska to Northern California (Fig. 1). It is declining in the northern part of its range due to a combination of factors associated with climate change and is a rare species in the southern part of its range in California and Southern Oregon. These southern populations are relics that occur in isolated stands in sub-alpine zones in cool wet sites at higher elevation > 5000 ft (Fig 2). The species is currently under review for listing as a threatened or endangered species.
Update 12/18
CBI finished cone collections in September, 2018, from six populations across three sites in Southern Oregon and three sites in Northern California. Access to other sites was restricted due to the Klondike Fire burning in Southern Oregon. This completes the first systematic collection of mature cones from these southern populations.
We have recieved word from the US Forest Service, Bend Seed Extractory, located in Bend Oregon, that they have successfully extracted viable seeds. The next step is to send them to the National Seed Laboratory in Dry Branch, Georgia, USA. Once there, these seeds will be entered into the the national germplasm bank making these the very first entries for these relic southern populations.
Needle tissue that was collected from 10 trees at each site will be genetically analyzed by researchers at the USFS Forest Science lab in Corvallis.This analysis will help determine if these populations are genetically distinct sub-populations from their northern counterparts which will help guide conservation of this species.
The Rogue River-Siskiyou National forest office is planning to use some of these seeds to grow seedlings to test for certain traits such as disease resistance and drought tolerance. The hope is that seeds collected from these southern populations may be used for restoration plantings in the northern regions.
In the north, Alaska Yellow Cedar is a valuable timber species but has been declining as a result of the climate crisis.
Conservation of these southern populations may prove to be critical for the longterm management of northern Alaska Yellow Cedars on public and private lands.
Fig 1. Range map for Alaska yellow cedar.
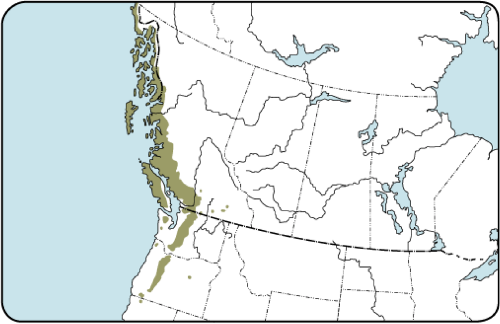
Source: http://tidcf.nrcan.gc.ca/en/trees/factsheet/376
Figure 2. Current known yellow cedar locations in the Siskyou Mountains (CBI 2017)